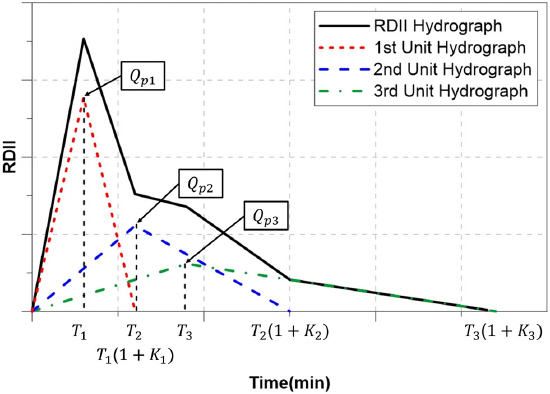
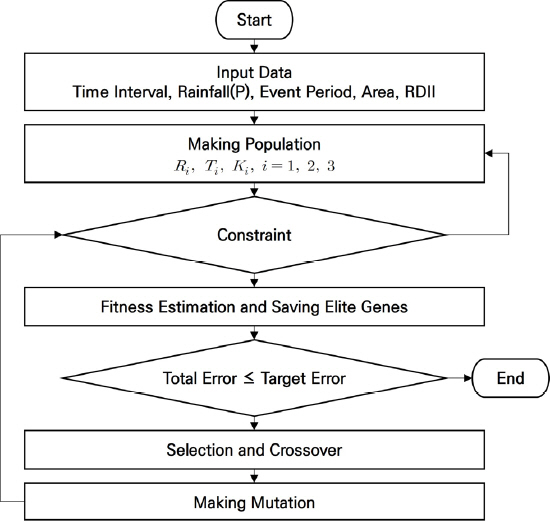
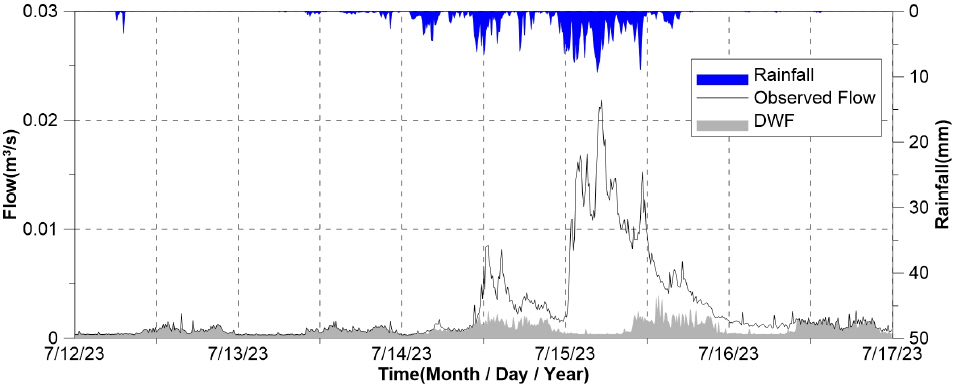
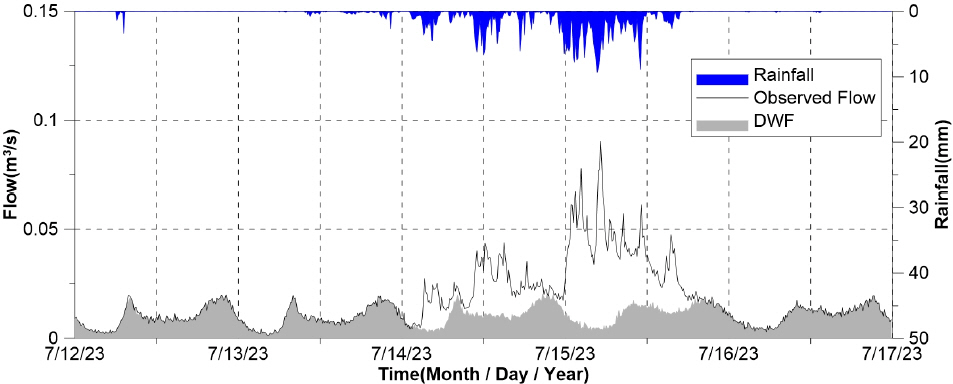
1. Bahng, E.Y (2010) Optimal sensor placement for structural parameter estimation using genetic algorithm. Journal of the Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 9-16.
2. Choi, I.H, and Choi, K.S (2016) A comparative study on sewage unit load with I/I and RDII. Journal of Korean Society of Environmental Technology, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 222-228.
3. Gromov, G, Ten, A, and Khudyakova, D (2018). Software analysis for the hydraulic calculation of storm-water drainage gravity-flow networks comprising electronic model development.
MATEC web of conferences. Vol. 251: p 03051. EDP Sciences.

4. Holland, J.H (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. Univ. MI Press.
5. Kim, J.R, Kim, J.H, and Oh, J.I (2016) Comparisons of RDII predictions using the RTK-based and regression methods.
Journal of Korean Society of Water and Wastewater, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 179-185.

6. Kim, J.Y, and Oh, J.I (2016) Assessment of design method about sanitary sewer network according RDII and established scenario.
Journal of Korean Society on Water Environment, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 367-374.

7. Lai, F.H (2008). Review of sewer design criteria and RDII prediction methods. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC.
8. Lee, J.H, Park, M.J, and Kim, J.H (2008) Rehabilitation priority decision model for sewer systems. Journal of the Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Vol. 8, No. 6, pp. 7-14.
9. Lee, Y.J, and Lee, C.Y (2021) Analysis of the inflow characteristics of separate sewer systems for rainfall using an XP-SWMM model and the SSOAP toolbox.
Journal of The Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 271-280.


10. Ministry of Environment (ME) and Korea Environment Corporation (KECO) (2018a) Guidelines for operation and management of separate sewer system in rainfall (plan).
11. Ministry of Environment (ME) and Korea Environment Corporation (KECO) (2018b) Guidelines for monitoring and modeling of sewage system in rainfall.
12. Ministry of Environment (ME) and Korea Environment Corporation (KECO) (2018c) A study on the effective sewage treatment plan in rainfall.
13. Ministry of Environment (ME) (2009) Standard manual for calculation of infiltration and inflow water in sewer pipes.
14. Shin, J.S, Han, S.W, Yook, J.S, Lee, C.G, and Kang, S.H (2019) Effect of infiltration/inflow by rainfall for sewerage facilities in the area with partially separate sewer system.
Journal of Korean Society of Water and Wastewater, Vol. 33, No. 3, pp. 177-190.

15. Staufer, P, Scheidegger, A, and Rieckermann, J (2012) Assessing the performance of sewer rehabilitation on the reduction of infiltration and inflow.
Water Research, Vol. 46, No. 16, pp. 5185-5196.


16. Vallabhaneni, S, Chan, C.C, and Burgess, E.H (2007). Computer tools for sanitary sewer system capacity analysis and planning. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH.
17. Zhang, K, and Parolari, A.J (2022) Impact of stormwater infiltration on rainfall-derived inflow and infiltration:A physically based surface-subsurface urban hydrologic model.
Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 610, pp. 127938.

18. Zhang, M, Liu, Y, Cheng, X, Zhu, D.Z, Shi, H, and Yuan, Z (2018) Quantifying rainfall-derived inflow and infiltration in sanitary sewer systems based on conductivity monitoring.
Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 558, pp. 174-183.