1. žĄú Ž°†
2. žīąŽč®Íłį žėąžł°žąėžúĄ žāįž†ē Žį©žēą
2.1 SWMM Í≤Ä‚čÖŽ≥īž†ē ŽĆÄžÉĀ Žß§ÍįúŽ≥Äžąė žĄ†ž†ē
2.2 Žß§ÍįúŽ≥Äžąė Í≤Ä‚čÖŽ≥īž†ēžĚĄ žúĄŪēú Žį©Ž≤ē
2.3 SWMMÍ≥ľ žĶúž†ĀŪôĒ ÍłįŽ≤ēžĚė žóįÍ≥Ą Žį©žēą
Table 2
| Superior Group | Population | Child Population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Population | Maintain | Change |
| Child Population | Maintain or Change | Change | |
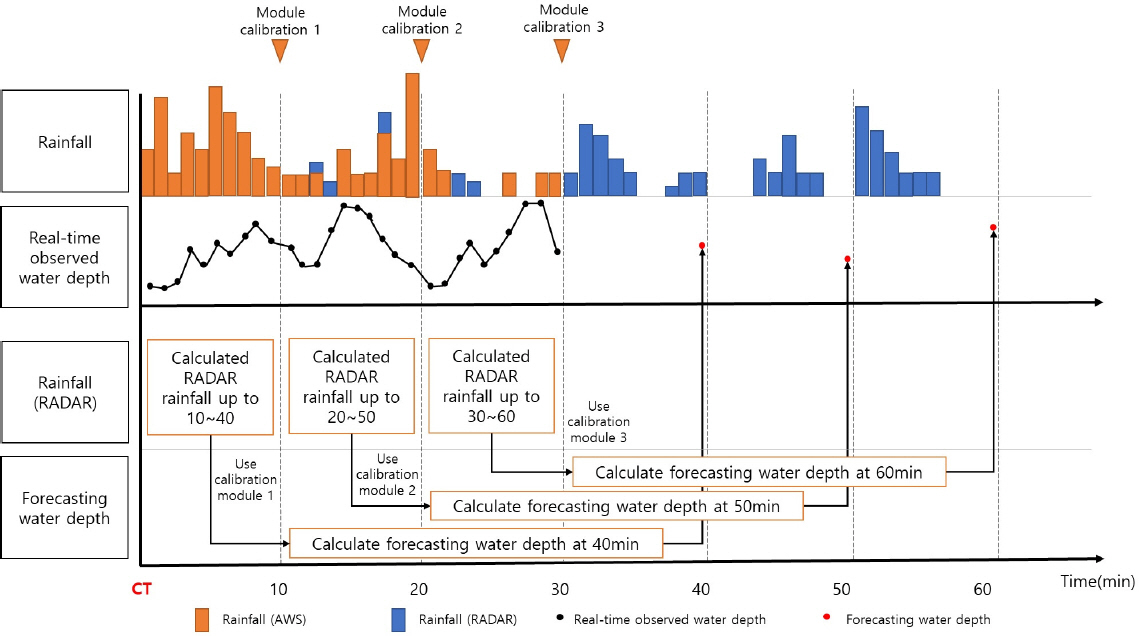
2.4 žīąŽč®Íłį žėąžł° žąėžúĄ žāįž†ē Í≥ľž†ē
(1) ŪėĄžě¨ žčúž†ź Íłįž§ÄžúľŽ°ú 0Ž∂ĄŽ∂ÄŪĄį 10Ž∂ĄÍĻĆžßÄ ÍīÄžł°Žźú žč§žčúÍįĄ žßÄžÉĀÍīÄžł°Íįēžöį(ASOS)žôÄ 2žčúÍįĄžĚė žĄ†ŪĖČÍįēžöįŽ•ľ žěÖŽ†•ŪēėÍ≥† 10Ž∂ĄžóźžĄúžĚė Ž™®žĚė žąėžúĄŽ•ľ žāįž†ēŪēúŽč§.
(2) Í≥ľž†ē (1)Ž≤ąžĚė Í≤įÍ≥ľžĚł 10Ž∂ĄžóźžĄú Ž™®žĚė žąėžúĄŽ•ľ 10Ž∂ĄžóźžĄú ÍīÄžł°Žźú žč§ž†ú žąėžúĄÍ≥Ą ÍīÄžł° žąėžúĄžôÄ ŽĻĄÍĶźŪēėžó¨ žĶúž†ĀŪôĒŽ•ľ žč§žčúŪēėÍ≥† Í≤įÍ≥ľ žóįÍ≥Ą Ž™®ŽďąžĚĄ ž†Äžě•ŪēúŽč§.
(3) Í≥ľž†ē (2)Ž≤ąžĚė žóįÍ≥Ą Ž™®ŽďąžĚĄ ÍłįŽįėžúľŽ°ú Í≥ľž†ē (1)Ž≤ąžóźžĄú žā¨žö©ŪēėžėÄŽćė žßÄžÉĀÍīÄžł°Íįēžöį(ASOS)žóź ž∂ĒÍįÄŽ°ú 30Ž∂Ą ŪõĄžĚė Ž†ąžĚīŽćĒ žėąžł° ÍįēžöįŽ•ľ žěÖŽ†•Ūēėžó¨ Íłįž°ī 10Ž∂ĄÍ≥ľ žėąžł° ÍįēžöįÍłįÍįĄ 30Ž∂Ą ŪõĄžĚł 40Ž∂ĄžóźžĄúžĚė žėąžł° žąėžúĄŽ•ľ žāįž†ēŪēúŽč§.
(4) Í≥ľž†ē (1)Ž≤ąžĚė 0Ž∂ĄŽ∂ÄŪĄį 10Ž∂ĄÍĻĆžßÄžĚė ÍīÄžł°Žźú Íįēžöįžóź 10Ž∂ĄŽ∂ÄŪĄį 20Ž∂ĄÍĻĆžßÄ ÍīÄžł°Žźú žč§žčúÍįĄ žßÄžÉĀÍīÄžł°Íįēžöį(ASOS)Ž•ľ žěÖŽ†•ŪēėÍ≥† Í≥ľž†ē (2)Ž≤ąžĚė žĶúž†ĀŪôĒ žóįÍ≥Ą Ž™®Žďąžóź ž†Āžö©ŪēúŽč§.
(5) Í≥ľž†ē (3)Ž≤ąÍ≥ľ ÍįôžĚī žĶúž†ĀŪôĒÍįÄ žôĄŽ£ĆŽźú žóįÍ≥Ą Ž™®Žďąžóź 30Ž∂Ą ŪõĄžĚė Ž†ąžĚīŽćĒ žėąžł° ÍįēžöįŽ•ľ žěÖŽ†•Ūēėžó¨ Íłįž°ī 30Ž∂ĄÍ≥ľ žėąžł° ÍįēžöįÍłįÍįĄ 30Ž∂Ą ŪõĄžĚł 50Ž∂ĄžóźžĄúžĚė žėąžł° žąėžúĄŽ•ľ žāįž†ēŪēúŽč§.
2.5 žīąŽč®Íłį žėąžł° žąėžúĄ ŪŹČÍįÄžßÄŪĎú žĄ†ž†ē
(2)
Table 3
| Performance rating | Very Good | Good | Satisfactory | Unsatisfactory |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basin Width | 0.75 < NSE ‚ȧ 1.00 | 0.65 < NSE ‚ȧ 0.75 | 0.50 < NSE ‚ȧ 0.65 | NSE ‚ȧ 0.5 |
3. Íįēžöį-žú†ž∂ú Ž™®Ūėē žěÖŽ†•žěźŽ£Ć ÍĶ¨ž∂ē
3.1 ŽĆÄžÉĀžú†žó≠
3.2 ÍįēžöįžčúŽāėŽ¶¨žė§ žĄ†ž†ē
Table 4
4. žč§ž†úžú†žó≠ ž†Āžö©
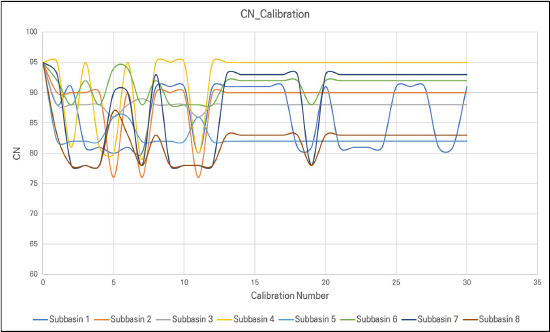
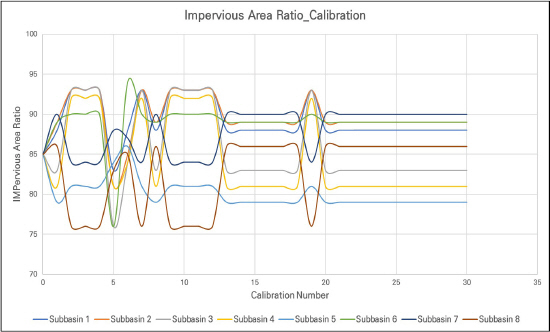
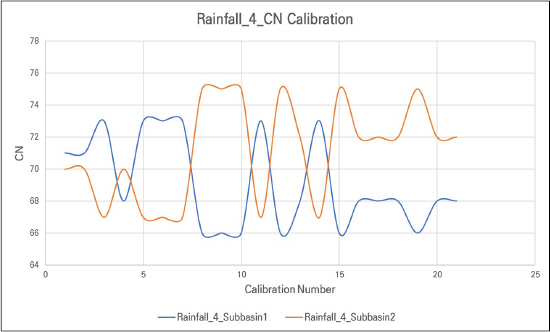
4.1 Žß§ÍįúŽ≥Äžąė žĶúž†ĀŪôĒ Í≤įÍ≥ľ
4.2 žóįÍ≥Ą Ž™®ŽďąžĚĄ žĚīžö©Ūēú žėąžł° žąėžúĄ žāįž†ē
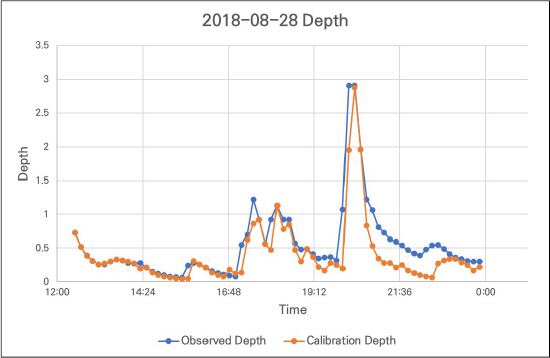
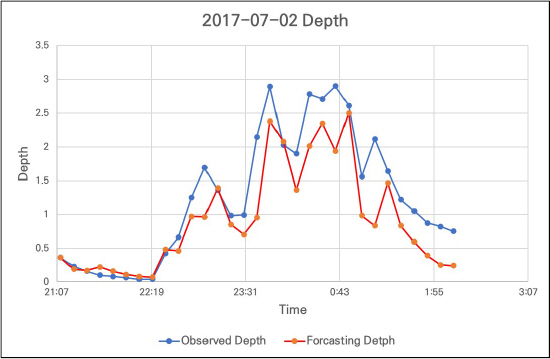
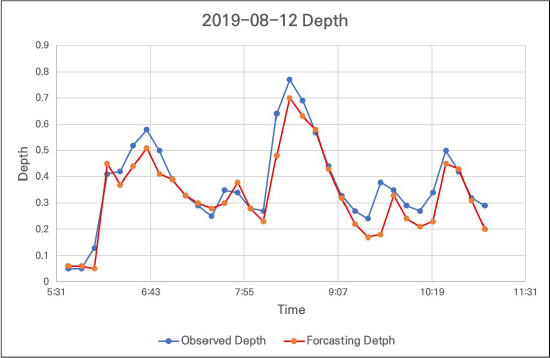
4.3 žėąžł° žąėžúĄ ž†ēŪôēŽŹĄ ŪŹČÍįÄ
Table 5
| Prameters | RMSE | NSE |
|---|---|---|
| Rainfall 1 | 0.496 | 0.713 |
| Rainfall 2 | 0.257 | 0.765 |
| Rainfall 3 | 0.06 | 0.825 |
| Rainfall 4 | 0.07 | 0.969 |