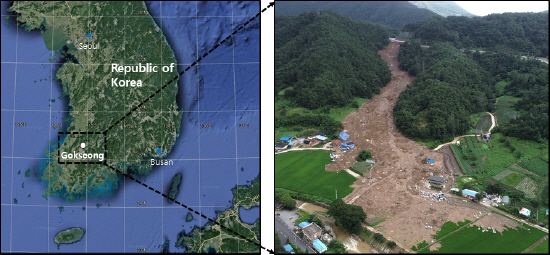
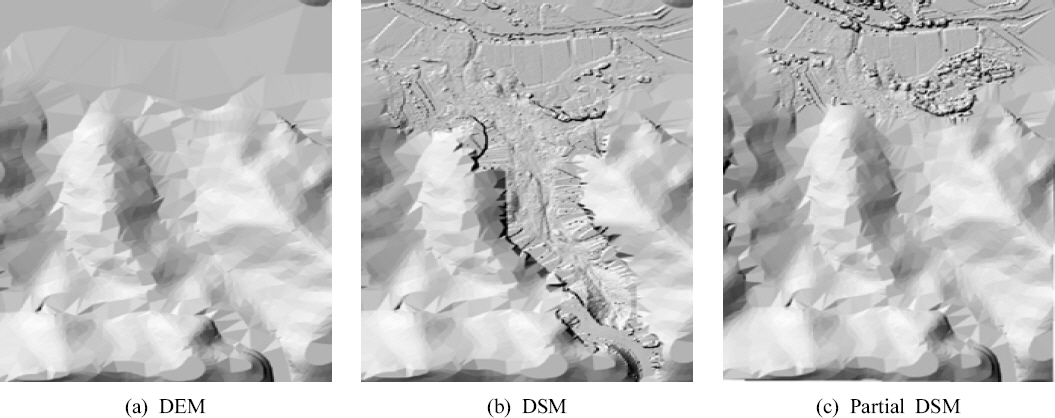
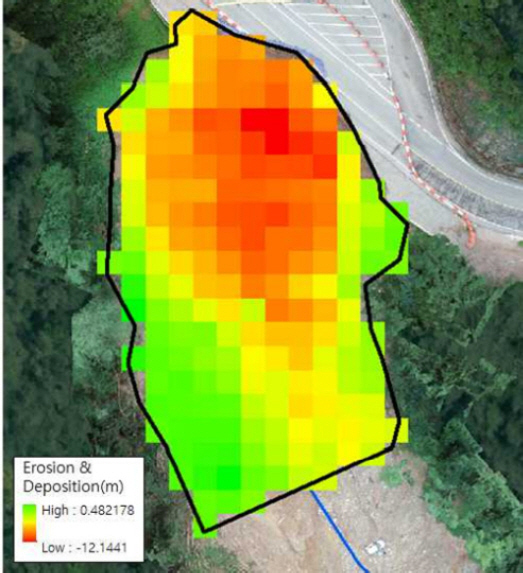
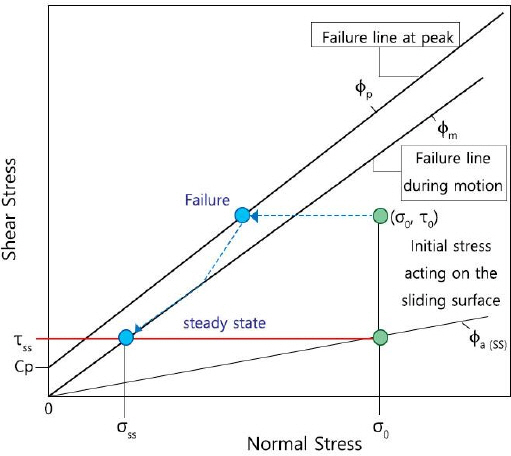
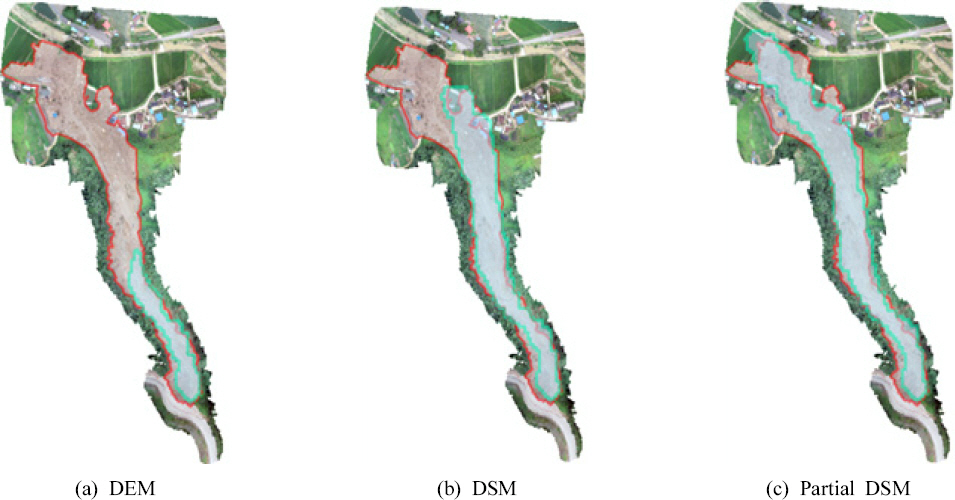
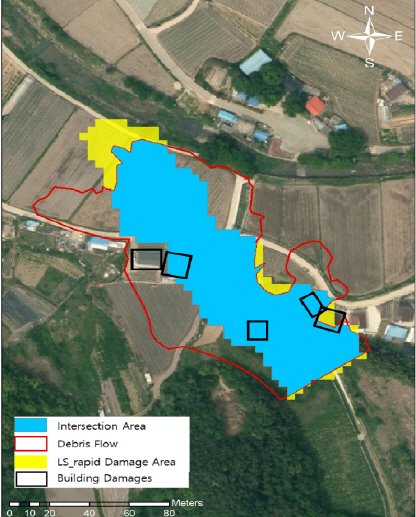
1. Capra, L, Manea, V.C, Manea, M, and Norini, G (2011) The importance of digital elevation model resolution on granular flow simulations:A test case for Colima volcano using TITAN2D computational routine.
Nat. Hazards, Vol. 59, pp. 665-680.


2. Chung, G.H, Jun, C.M, Kwon, J.H, and Jeon, C.D (2007) A study on the error detection of attached cadastral maps using GIS.
Journal of the Korean Society of Cadastre, Vol. 23, No. 2, pp. 47-55.

3. Cruden, D.M, and Varnes, D.J (1996) Landslide types and processes. In Landslides:Investigation and mitigation.
Transportation Research Board, Special Report 247, pp. 36-75.

4. Evans, S.G, Hungr, O, and Enegren, E.G (1994) The avalanche lake rock avalanche, mackenzie mountains, northwest territories, Canada:Description, dating, and dynamics.
Canadian Geotechnical Journal, Vol. 31, No. 5, pp. 749-768.

5. Gradiški, K, Sassa, K, He, B, Arbanas, Ž, MihalićArbanas, S, Krkač, M, et al (2013) Application of integrated landslide simulation model LS-Rapid to the Kostanjek Landslide, Zagreb, Croatia.
Proceedings of the 1st Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic Balkan Region, pp. 11-16.

6. Heim, A (1989).
Landslide &human lives. Vancouver: Bi-Tech Publishers.

7. Horton, P, Jaboyedoff, M, Rudaz, B, and Zimmermann, M (2013) Flow-R, a model for susceptibility mapping of debris flows and other gravitational hazards at a regional scale.
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci, Vol. 13, pp. 869-885.

8. Hsu, K.J (1975) Catastrophic debris streams (sturzstroms) generated by rockfalls.
Geological Society of America Bulletin, Vol. 86, No. 1, pp. 129-140.

9. Hungr, O (1995) A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and avalanches.
Canadian Geotechnical Journal, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 610-623.

10. Jovančević, S.D, Nagai, O, Sassa, K, and Arbanas, Ž (2014) Deterministic landslide susceptibility analyses using ls-rapid software.
The First Regional Symposium on Landslides in Adrian-Balkan Region, pp. 73-77.

11. Lee, J.Y, Kim, D.K, Park, K.W, and Kim, T.W (2019) Establishment of accuracy criteria of flood inundation map using quantitative evaluation indices.
Journal of the Korean Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. 39, No. 3, pp. 381-389.

12. Miura, H (2019) Fusion analysis of optical satellite images and digital elevation model for quantifying volume in debris flow disaster.
Remote Sens, Vol. 11, No. 9, pp. 1096-1115.

13. Rabby, Y.W, Ishtiaque, A, and Rahman, M (2020) Evaluating the effects of digital elevation models in landslide susceptibility mapping in rangamati district.
Bangladesh. Remote Sens, Vol. 12, No. 17, pp. 2718-2753.

14. Rickenmann, D (2016) Debris-flow hazard assessment and methods applied in engineering practice.
International Journal of Erosion Control Engineering, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 80-90.

15. Sarmaa, C.P, Deya, A, and Krishna, A (2020) Influence of digital elevation models on the simulation of rainfall- induced landslides in the hillslopes of Guwahati, India.
Engineering Geology, Vol. 268, pp. 105523.

16. Sassa, K (1988) Geotechnical model for the motion of landslides, proceedings 5th international symposium on landslides.
Landslides, Vol. 1, pp. 37-56.

17. Sassa, K, Nagai, O, Solidum, R, Yamazaki, Y, and Ohta, H (2010) An integrated model simulating the initiation and motion of earthquake and rain induced rapid landslides and its application to the 2006 Leyte landslide.
Landslides, Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 219-236.


18. Setiawan, H, Wilopo, W, Fathani, T.F, and Karnawati, D (2019) Analysis of potential landslide and its motion behavior in Salem District, Brebes Regency, Central Java of Indonesia by using the LS-RAPID numerical simulation.
Landslides, Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 2219-2232.


19. Stefanescu, E.R, Bursik, M, and Patra, A.K (2012) Effect of digital elevation model on Mohr-Coulomb geophysical flow model output.
Nat. Hazards, Vol. 62, pp. 635-656.


20. Stolz, A, and Huggel, C (2008) Debris flows in the Swiss National Park:The influence of different flow models and varying DEM grid size on modeling results.
Landslides, Vol. 5, pp. 311-319.


21. Wechsler, S.P (2007) Uncertainties associated with digital elevation models for hydrologic applications:A review.
Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci, Vol. 11, pp. 1481-1500.