1. 서 론
1.1 연구의 배경
1.2 연구의 목적
2. 재해 회복력 측정에 대한 선행연구
2.1 회복력 개념에 대한 고찰
Table 1
Table 2
| Approach | Author | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Resilience | Timmerman (1981) | - The ability of system to absorb and recover from hazardous event |
| Pimm (1984) | - The speed at which the system returns to its original state after a disaster, a concept related to the functioning of the system itself rather than the stability of system components | |
| Wildavsky (1988) | - The ability to overcome unexpected shocks | |
| Kang et al. (2007) | - The ability of a system to recover to its pre-disaster state, measured by left duration of its unstable state | |
| Cardona (2003) | - The ability of systems that have been damaged by disasters to absorb negative effects and recover | |
| Bruneau et al. (2003) | - A concept that includes preparation to prevent damage before disaster, planning activities that can minimize negative impacts of disaster | |
| Zhou et al. (2010) | - The ability to resist and recover from losses caused by shocks | |
| Ecological Resilience | Mileti (1999) Buckle et al. (2000) | - The ability of a system to withstand extreme conditions without significant external support and without significant loss, damage, productivity, or reduced quality of life |
| Adger (2003) | - The ability of a system to maintain its function and structure from shocks and disturbances, and to continue to provide essential resources and ecosystems for livelihood | |
| Paton and Johnston (2001) Paton et al. (2008) | - Analyze the ability to resist based on trust in government, self-efficacy, risk perception and expectations, based on individual motivation to prepare for and act in risky situations | |
| Twigg (2009) | - Organize the influencing factors such as regional and community governance, risk assessment, knowledge and education, risk management and vulnerability reduction, disaster preparedness and response, and actions that affect the impact of a disaster | |
| Ecological& Evolutionary Resilience | Geis (2000) Chen et al. (2008) | - The ability to resist shock or to recover or adapt quickly after a shock |
| Nelson (2010) |
- Analyze conceptual agreements and conflicts between resilience and climate change adaptation - Researching that adaptation after disasters at a local scale can affect resilience across larger systems |
|
| Evolutionary Resilience | Klein et al. (2003) Folke (2006) Cutter et al. (2008) Adger et al. (2005) |
- The ability to absorb the impact of a disaster and to reorganize and adapt so that social systems can fully function - The ability to return to a pre-damage state as well as progress to a better state through learning and adaptation |
| Manyena (2006) Manyena et al. (2011) |
- Focus on recovery and leaps, rather than just resistance to shock - The ability to effectively adapt to disturbances and move on to the better |
|
| UNISDR (2009) | - The ability of disaster-damaged systems to resist, absorb, adapt, and recover from disasters through timely preservation and restoration of structures and functions |
2.2 회복력의 측정과 평가 지표 연구
Table 3
Table 4
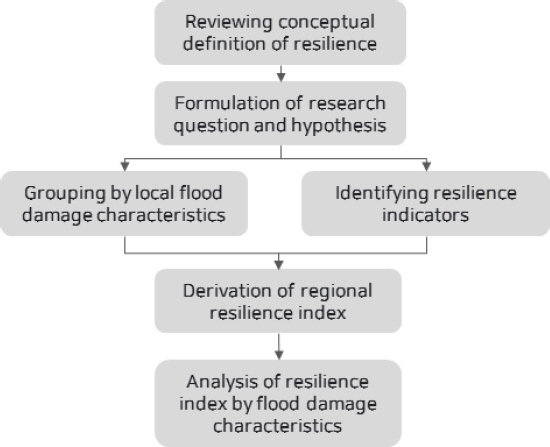
3. 연구의 설계
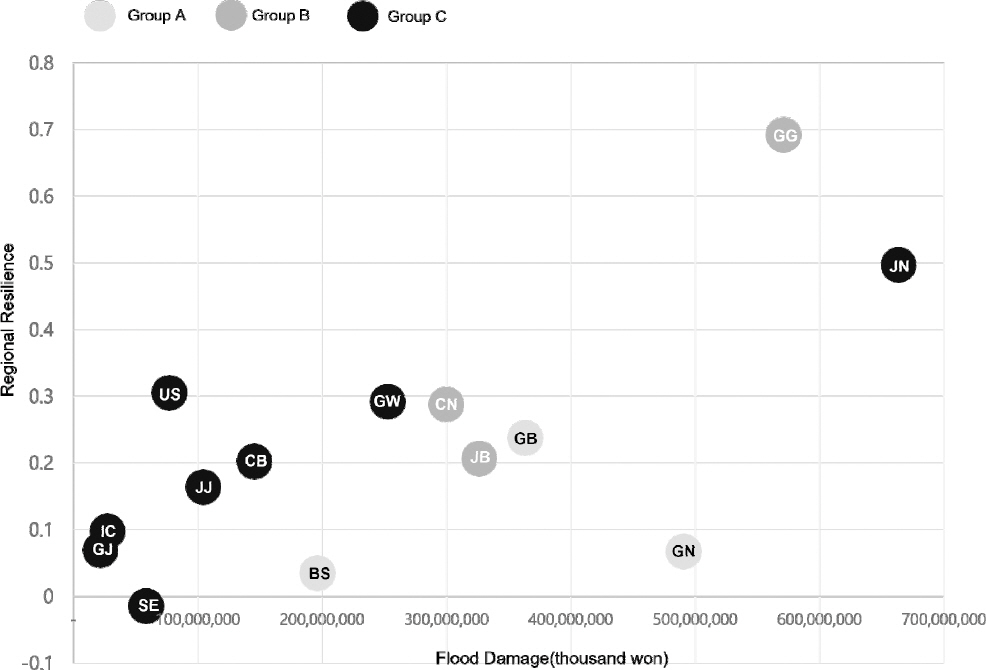
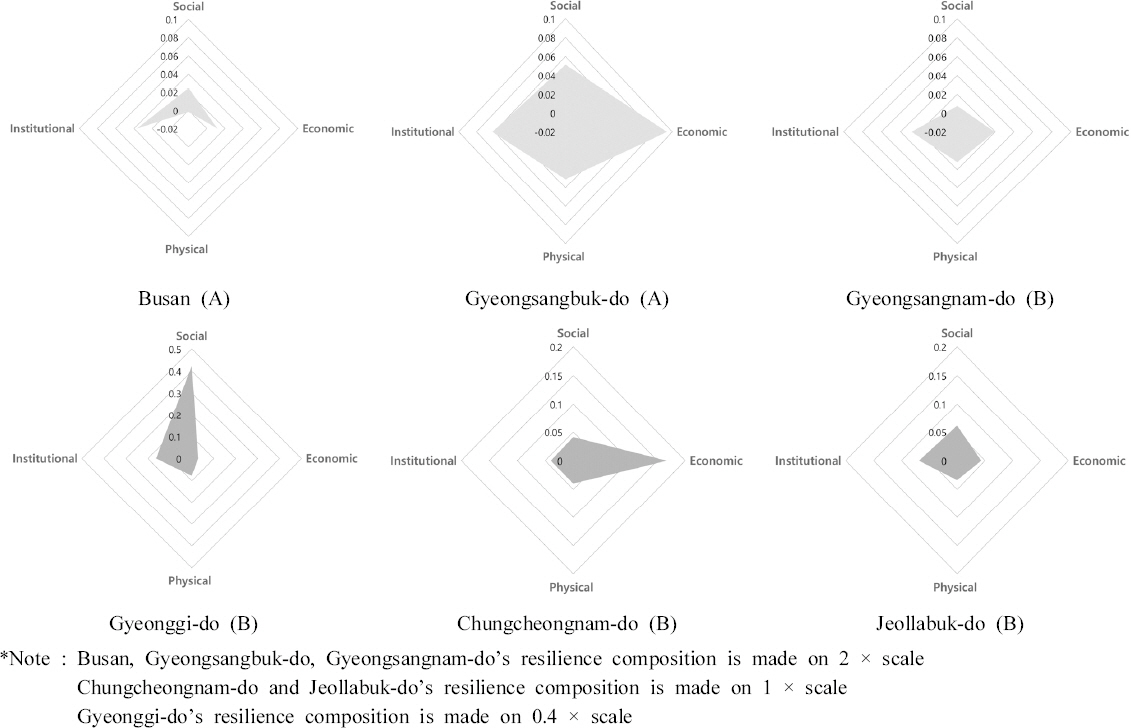
3.1 연구질문 및 가설 설정
3.2 연구의 범위 및 분석자료
3.2.1 연구의 범위
Table 5
3.2.2 분석자료
Table 6
| Type | Indicator | Explanation | Potential Impact | Direction | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Resilience | Vulnerable | 65 years or older (%) under 6 years old (%) | Resistance Adaptation | Negative | Fu et al. (2016) |
| Social capital | NGO per 10,000 people | Adaptation | Positive | Cutter et al. (2010) | |
| Public space | Open space per person (m2) | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Cox and Hamlen (2015); Fu et al. (2016) | |
| Level of education | University graduates (%) | Adaptation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016); Cox and Hamlen (2015) | |
| Economic Resilience | Employment rate | Employment rate (%) | Adaptation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016); Cutter et al. (2010) |
| Income | GRDP per person | Adaptation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016); Cutter et al. (2010) | |
| Commercial facility | Commercial facilities per 100,000 people | Adaptation | Positive | Cutter et al. (2008) | |
| Home ownership | Own rate of housing (%) | Mitigation | Positive | Cutter et al. (2010) | |
| Energy consumption | Energy consumption per capita (TOE) | Mitigation | Negative | Rosales (2011); Fu et al. (2016) | |
| Physical Resilience | Green | Green area per person (m2) | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Adger (2006) |
| Park | Park area per person (m2) | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Adger (2006) | |
| Farmland | Ratio of farmland (m2) | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016) | |
| Sewage | Sewer penetration rate (m2) | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Wehmeyer et al. (2011) | |
| Old building | Ratio of buildings older than 35 years (%) | Resistance | Negative | Mileti (1999) | |
| Urbanization | Urbanization rate (%) | Resistance | Negative | Fu et al. (2016) | |
| Institutional Resilience | Shelter | Shelters per 10,000 people | Mitigation | Positive | Tierney (2009); Hung et al. (2016); Cutter et al. (2010) |
| Land use | Conservation area per person | Resistance Mitigation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016) | |
| Fire and police | Fire and police stations per 10,000 people | Mitigation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016); Cox and Hamlen (2015) | |
| Medical service | General hospital per 10,000 people | Mitigation | Positive | Hung et al. (2016); Cutter et al. (2010) |