1. ņä£ ļĪĀ
2. ņŗżĒŚśĻ│äĒÜŹ ļ░Å ļ░®ļ▓Ģ
2.1 ņŗżĒŚśĻ│äĒÜŹ
Table┬Ā1
| Test | P:M | W/B (%) | R (%) | Curing period | Measurement item (Standard of measurement) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
1:0.5 1:1.0 1:1.5 1:2.0 1:2.5 1:3.0 |
30 | - |
15 min., 30 min., 60 min., 1 Day, 3 Days, 7 Days, 14 Days, 28 Days |
ŌŚå Flow table (KS L 5111, 2017) ŌŚå Hardening time - Visual observation ŌŚå Hydration heat (KS L 5121, 2017) ŌŚå Compressive strength (KS L 5105, 2017) ŌŚå Bending strength (KS F 2408, 2016) ŌŚå SEM (After 28 Days) |
| 2 | 1:1.5 | 30 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
2.2 ņé¼ņÜ®ņ×¼ļŻī ļ░Å ņŗ£ĒŚśņ▓┤ ņĀ£ņ×æ
Table┬Ā2
| Appearance | Purity | pH (1% solŌĆÖn) | Sulfate (SO4) | Iron (Fe) |
| White Crystal | 98.0% up | 4.2-4.7% | 0.02% max | 0.01% max |
Table┬Ā3
| Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Ti | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zn | Sn |
| 86.3 | 0.66 | 2.69 | 1.08 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 3.26 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
3. ņ×¼ļŻīĒŖ╣ņä▒ņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝
3.1 CBPCņØś ĻĄ│ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņä▒ņāü
3.2 CBPCņØś ĻĄ│ņØĆ ņä▒ņāü
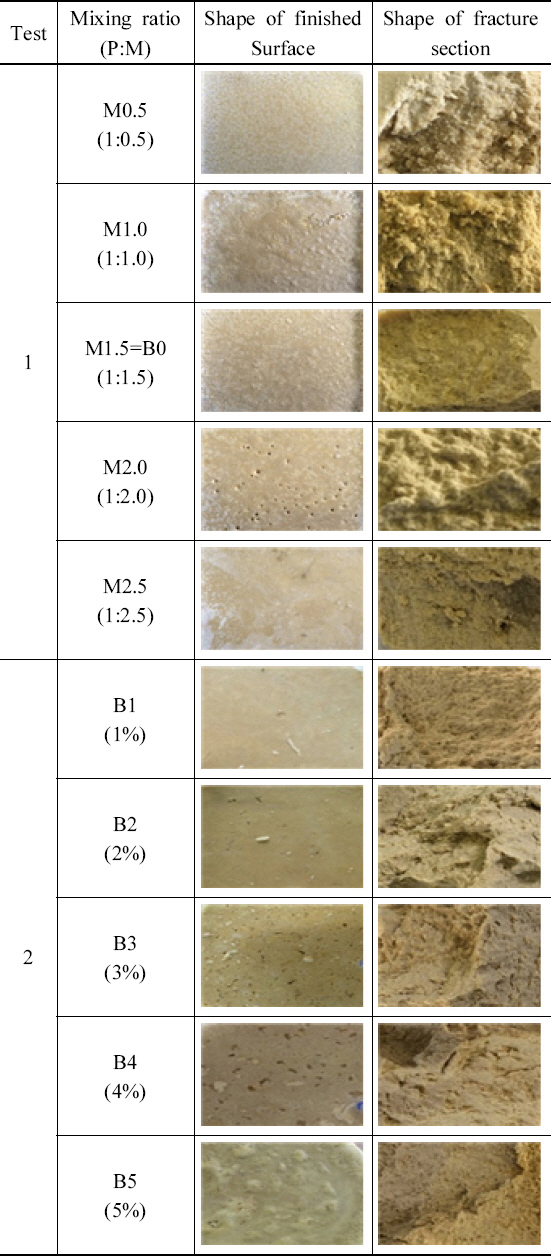
3.2.1 ņŗ£ĒŚśņ▓┤ņØś Ēæ£ļ®┤ ļ░Å ĒīīĻ┤┤ņĀłļŗ©ļ®┤
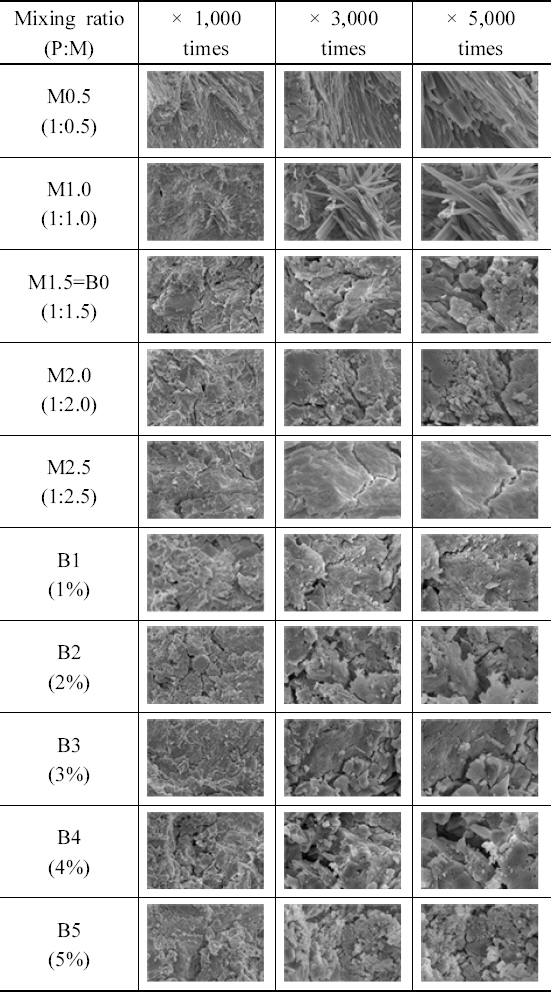
3.2.2 SEM ņ┤¼ņśüĻ▓░Ļ│╝
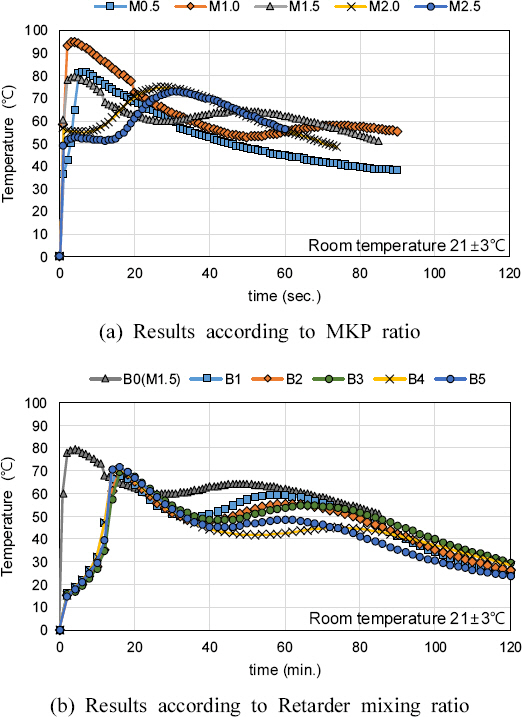
3.3 MKPļ░░ĒĢ®ļ╣äņ£©ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ļ░£ņŚ┤ ĒŖ╣ņä▒
3.4 CBPCņØś ņŚŁĒĢÖņĀü ĒŖ╣ņä▒
4. Ļ▓░ ļĪĀ
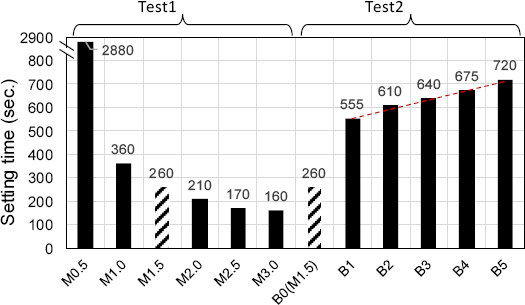
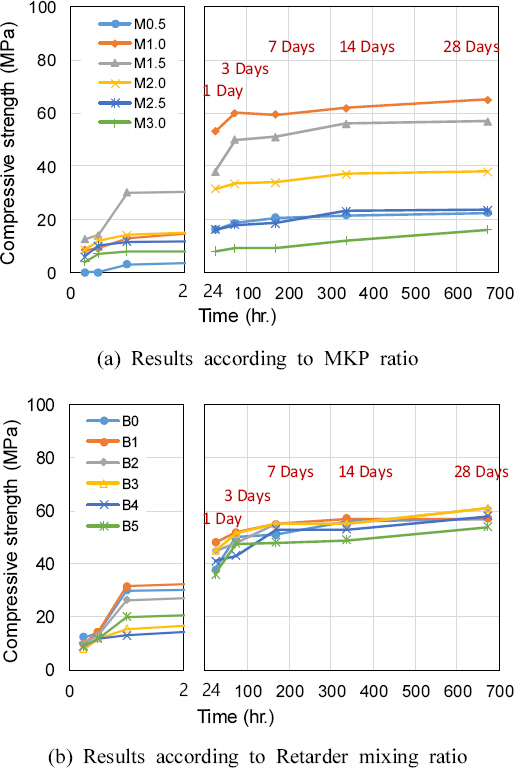
ņ£ĀļÅÖņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ▓ĮĒÖöņŗ£Ļ░ä Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ M1.0~2.5ņØś ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņØ┤ ņŗ£Ļ│Ąņä▒Ļ│╝ ņĢłņĀĢņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢ£ ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ļ░░ĒĢ®ļ▓öņ£äļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉśļ®░, M2.0 ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļ░░ĒĢ®ņŚÉņä£ļŖö Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉ ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ│ĄĻĘ╣ņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņä£ ļ¦łĻ░Éņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśļ®┤ ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ļ░░ĒĢ® ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ░░ņĀ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņ¢æņāØĻĖ░Ļ░ä 28ņØ╝ņŚÉ ņĢĢņČĢĻ░ĢļÅä 40 MPa ņØ┤ņāü ļ░£ĒśäĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ¬®Ēæ£ Ļ░Æņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżņĀĢĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ļ¬©ļōĀ ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ ļ¬®Ēæ£ Ļ░ÆņØä ņāüĒÜīĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ņØ┤ ņżæ ņĪ░ĻĖ░ ņĢĢņČĢĻ░ĢļÅä ļ░£Ēśä ĒŖ╣ņä▒ ļ░Å ņĄ£ļīĆņĢĢņČĢĻ░ĢļÅäĻ╣īņ¦Ć Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśļ®┤ M1.5ņØś ļ░░ĒĢ®ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ Ļ░Ćņן ņóŗņØĆ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņĀ£ Ēś╝ņ×ģņ£©ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļ®┤ Ēæ£ļ®┤ ļ¦łĻ░Éņä▒ļŖźņØ┤ ņóŗņ¦Ć ņĢŖņ£╝ļ®░, ņĢĢņČĢĻ░ĢļÅä ļ░Å Ē£©Ļ░ĢļÅäĻ░Ć ļŗżņåī Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
MKPļ░░ĒĢ®ļ╣ä M1.5ļź╝ ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņĀ£ļź╝ 1%ļ¦ī Ēś╝ņ×ģĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļŖö ņ£ĀļÅÖņä▒ ņ”ØĻ░Ć, Ļ▓ĮĒÖöņŗ£Ļ░ä ņ”ØĻ░Ć ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņĢĢņČĢĻ░ĢļÅä ņ”ØĻ░ĆņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
CBPCļ│ĄĒĢ®ņ▓┤ņØś ņŻ╝ņÜö ņøÉļŻīĻ░Ć ļÉśļŖö ņØĖņé░ņŚ╝Ļ│╝ ļ¦łņŖżļäżņŖśĻ│╝ņØś ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ļ░░ĒĢ®ļ╣ä 1:1.5Ļ░Ć ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ļ░░ĒĢ®ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉśļ®░, ņ¦ĆņŚ░ņĀ£ Ēś╝ņ×ģņ£©ņØĆ 1~2%ņØś ļ▓öņ£äņŚÉņä£ ņ£ĀļÅÖņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĀüņĀłĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉ£ļŗż.