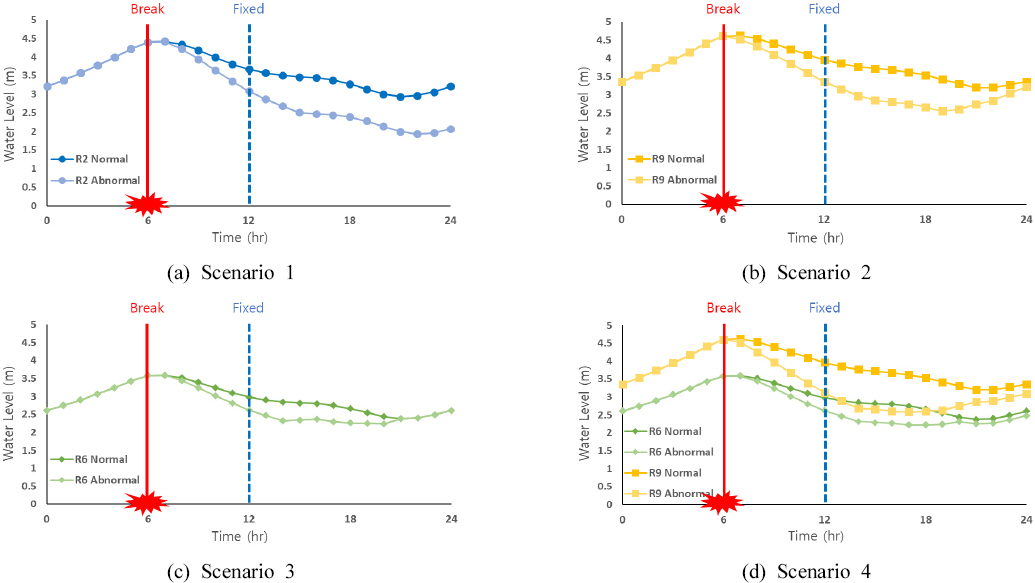
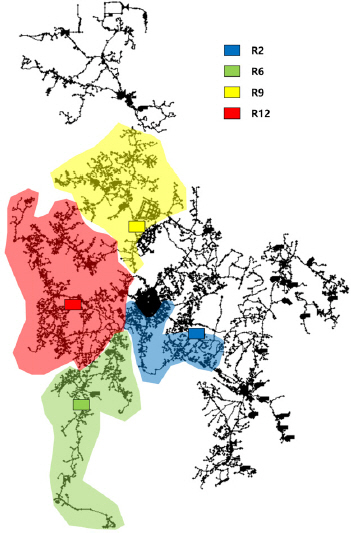
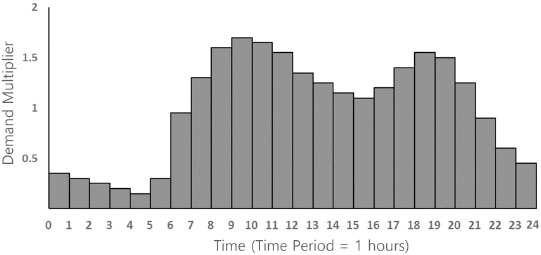
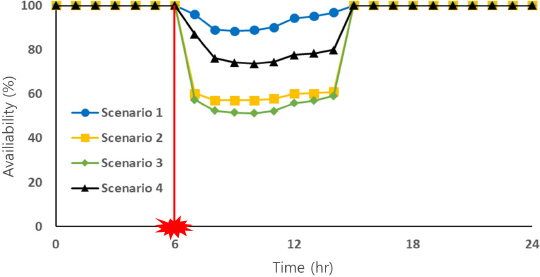
1. Baek, C.W, Kim, S.W, Kim, E.S, Kim, J.H, and Park, M (2006) Development of optimal decision-making system for rehabilitation of water distribution systems divided by small division.
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association, Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 545-552.


2. Cullinane, M.J, Lansey, K.E, and Mays, L.W (1992) Optimization-availability-based design of waterdistribution networks.
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 118, No. 3, pp. 420-441.

3. Environmental Protection Agency (2011)
Planning for an Energency Drinking Water Supply.

4. Fujiwara, O, and Ganesharajah, T (1993) Reliability assessment of water supply systems with storage and distribution networks.
Water Resources Research, Vol. 29, No. 8, pp. 2917-2924.

5. Germanopoulos, G (1985) A technical note on the inclusion of pressure dependent demand and leakage terms in water supply network models.
Civil Engineering Systems, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 171-179.

6. Gupta, R, and Bhave, P.R (1996) Comparison of methods for predicting deficient-network performance.
Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, Vol. 122, No. 3, pp. 214-217.

7. Kim, S, Gim, A, Ha, J, and Jun, H (2020) Determination of proper water supply rate for emergency interconnection plan.
J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 20, No. 6, pp. 159-166.


8. Lee, H.M, Jun, H, Back, S.C, and Kim, J.H (2018) Development and application of advanced-pressure driven analysis model considering limited reservoir.
J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 271-280.


9. Lee, H.M, Shin, E, and Kim, J.H (2018) Development applications of K-NRisk for pressure dependent demand analysis in water distribution networks.
J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 231-238.


10. Lee, T.K, Chae, S.H, Kim, S.S, Seo, I.S, Kim, J.H, and Park, N.S (2012) Establishment of methodology for estimating an emergency water.
Journal of Korean Society of Water and Wastewater, Vol. 26, No. 3, pp. 361-372.


11. Ministry of Environment (ME) (2010)
Design standard for water distribution systems.

12. Ministry of Environment (ME) (2015)
Guidelines for the establishment of a basic plan for water maintenance.

13. Ministry of Environment (ME) (2021)
Statistics of waterworks.

14. Oak, S, Kim, S, and Jun, H (2018) An application of the A-PDA model and the water supply performance index for the temporal and spatial evaluation of the performance of emergency water supply plans via interconnections.
Journal of Korea Water Resources Association, Vol. 51, No. 11, pp. 977-987.

15. Rossman, L.A (2000) EPANET 2:Users manual.
Cincinnati, OH:EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency).

16. Tanyimboh, T.T, and Templeman, A.B (2004) A new nodal outflow function for water distribution networks.
Proceedings of the 4th International Conf. on Eng. Computational Technology, Civil-Comp Press, Stirling, UK, Paper. Vol. 64, pp. 12.

17. Udo, A (2001) Steady-state flow analysis of pipe networks considering reduction of outflow in the case of low water pressures.
Water Software Systems, Vol. 1, pp. 173-182.

18. Wagner, J.M, Shamir, U, and Marks, D.H (1988) Water distribution reliability:Simulation methods.
Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, Vol. 114, No. 3, pp. 276-294.

19. Yoo, D.G, Kim, K.P, Park, M.J, and Joo, J.G (2017) Multi-objective optimal design for improving water supply serviceability considering segments in water distribution networks.
J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 29-37.

20. Yoo, D.G, Lee, S.Y, Lee, H.M, Jun, H, and Kim, J.H (2015) Life cycle energy analysis of pipe rehabilitation and replacement strategies in water pipeline systems.
J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 301-310.