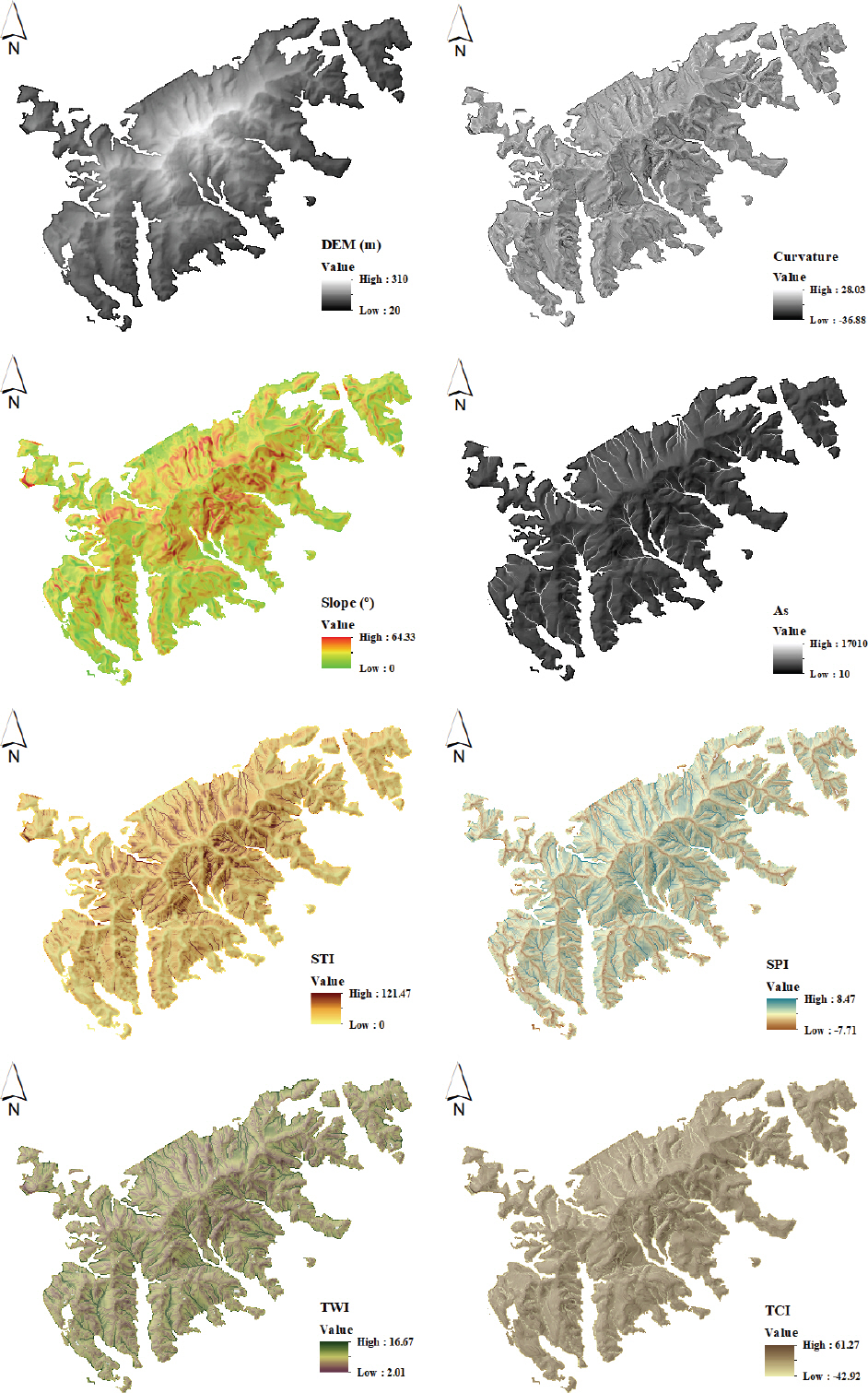
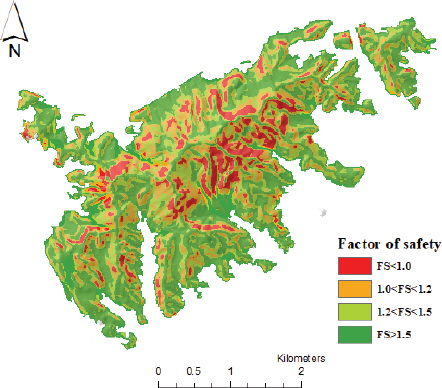
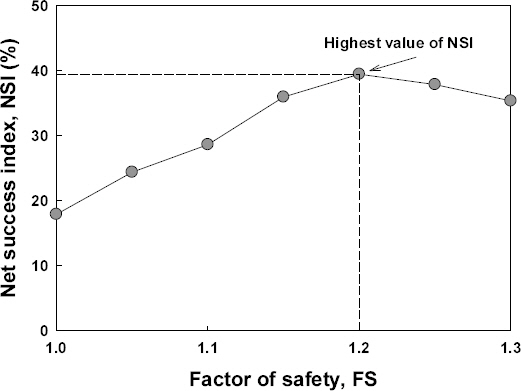
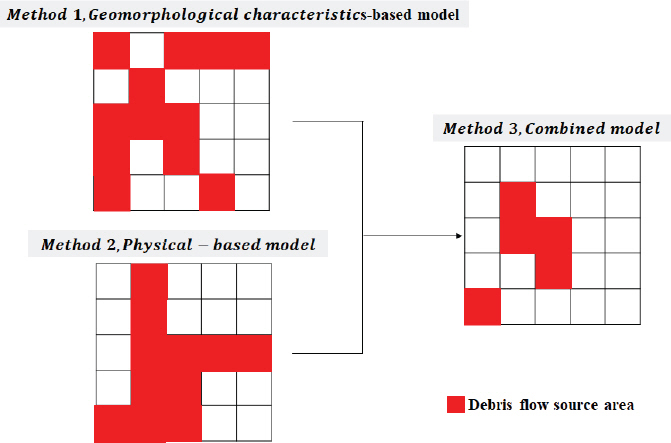
1. Baum, R.L, Godt, J.W, and Savage, W.Z (2010) Estimating the timing and location of shallow rainfall-induced landslides using a model for transient, unsaturated infiltration.
Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 115, No. F03013, pp. 1-26.

2. Blahut, J, van Westen, C.J, and Sterlacchini, S (2010) Analysis of landslide inventories for accurate pre- diction of debris-flow source areas.
Geomorphology, Vol. 119, pp. 36-51.

3. Brayshaw, D, and Hassan, M.A (2009) Debris flow initiation and sediment recharge in gullies.
Geomorphology, Vol. 109, pp. 122-131.

4. Choi, W.I, Choi, E.H, and Baek, S.C (2017) Analysis of hazard area by sediment disaster prediction techniques based on ground characteristics.
Korea Geo-Envirnmental Society, Vol. 18, No. 12, pp. 47-57.

5. Crosta, G.B, and Frattini, R (2003) Distributed modelling of shallow landslides triggered by intense rainfall.
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci, Vol. 3, pp. 81-93.


6. Delmonaco, G, Leoni, G, Margottini, C, Puglisi, C, and Spiz zichino, D (2003) Large scale debris-flow hazard assessment:A geotechnical approach and GIS modeling.
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., Vol. 3, pp. 443-455.


7. Fischer, L, Rubensdotter, L, Sletten, K, Stalsberg, K, Melchiorre, C, Horton, P, et al (2012) Debris flow modeling for susceptibility mapping at regional to national scale in Norway. Proceedings of the 11th International and 2nd NorthAmerican Symposium on Landslides; Banff, Alberta, Canada.

8. Godt, J.W, Baum, R.L, Savage, W.Z, Salciarini, D, Schulz, W.H, and Harp, E.L (2008) Transient deterministic shallow landslide modeling:Requirements for susceptibility and hazard assessments in a GIS framework.
Eng Geol, Vol. 102, pp. 214-226.

9. Griswold, J.P, and Iverson, R.M (2008) Mobility and statistics and automated hazard mapping for debris flows and rock avalanches.
U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2007-5276, pp. 59.

10. Horton, P, Jaboyedoff, M, and Bardou, E (2008). Debris flow susceptibility mapping at a regional scale. Proc. of the 4th Canadian Conference on Geohazards, Quebec, Canada: p 339-406.

11. Iverson, R.M (2000) Landslide triggering by rain infiltration.
Water Resources Research, Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 1897-1910.

12. Jun, K.W, and Oh, C.Y (2011) Study on risk analysis of debris flow occurrence basin using GIS.
The Korean Society of Safety, Vol. 26-2, pp. 83-88.

13. Kang, H.S, and Kim, Y.T (2015) Study on physical vulnerability curves of buildings by numerical simulation of debris flow.
Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Vol. 15, No. 5, pp. 155-167.

14. Kang, S.H, and Lee, S.R (2018) Debris flow susceptibility assessment based on an emprical approach in the central region of South Korea.
Geomorphology, Vol. 308, pp. 1-12.

15. Kang, S.H, Lee, S.R, Nikhil, N.V, and Park, J.Y (2015) Analysis of differences in geomorphological charac- teristics on initiation of landslides and debris flows.
Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 249-258.


16. Kappes, M.S, Malet, J.P, Remaitre, A, Horton, P, Jaboyedoff, M, and Bell, R (2011) Assessment of debris-flow susceptibility at medium-scale in the Barcelonnette Basin, France.
Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, Vol. 11, pp. 627-641.


17. Kim, G.H, Yune, C.Y, Lee, H.G, and Hwang, J.S (2011) Debris flow analysis of landslide area in Inje using GIS.
Korean Society of Surveying Geodesy Photo- grammetry and Cartography, Vol. 29, pp. 47-53.


18. Kim, K.S (2008) Characteristics of basin topography and rainfall triggering debris flow.
Korean society of civil engineers, Vol. 28, No. 5, pp. 263-271.

19. Kim, N.G, Kim, M.I, Kwak, J.H, and Jun, B.H (2019) Analysis of the topography characteristics of a debris-flow area using drones.
KOSHAM, Vol. 4, pp. 127-133.


20. Kim, P.G, and Han, K.Y (2017) Numerical modeling for the detection of debris flow using detailed soil map and GIS.
Korean Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. 37, No. 1, pp. 43-59.

21. Lee, H.N, and Kim, G.H (2020) Analysis of topographical factors in woomyun mountain debris flow using GIS.
KSIC, Vol. 23, No. 5, pp. 809-815.

22. Lee, M.J, and Kim, Y.T (2013) Movement and deposition characteristics of debris flow according to rheological factors.
Korean Geotechnical Society, Vol. 29, No. 5, pp. 19-27.

23. Lorente, A, Garcia-Ruiz, J.M, Begueria, S, and Arnaez, J (2002) Factors explaining the spatial distribution of hillslope debris flows.
Mountain Research and Development, Vol. 22, No. 1, pp. 32-39.

24. Meyer, N.K, Schwanghart, W, Korup, O, Romstad, B, and Etzelmuller, B (2014) Estimating the topographic predictability of debris flows.
Geomorphology, Vol. 207, pp. 114-125.

25. Nam, D.H, Lee, S.H, Kim, M.I, and Kim, B.S (2018) Calculation of rainfall triggering index (RTI) to predict the occurrence of debris flow.
Engineering Geology, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 47-59.

26. Rickenmann, D, and Zimmermann, M (1993) The 1987 debris flows in Switzerland:Documentation and analysis.
Geomor Phology, Vol. 8, No. 2-3, pp. 175-189.

27. Salciarini, D, Godt, J.W, Savage, W.Z, Conversini, P, Baum, R.L, and Michael, J.A (2006) Modeling regional initi ation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the eastern Umbria region of central Italy.
Landslides, Vol. 3, pp. 181-194.


28. Salciarini, D, Tamagnini, C, Conversini, P, and Rapinesi, S (2012) Spatially distributed rainfall thresholds for the initiation of shallow landslides.
Natural Hazards, Vol. 61, No. 1, pp. 229-245.


29. Si, A, Zhang, J, Zhang, Y, Kazuva, E, Dong, Z, Bao, Y, et al (2020) Debris flow susceptibility assessment using the integrated random forest based steady-state infinite slope method:A case study in changbai mountain.
China, Water, Vol. 12, pp. 2057.

30. Sorbino, G, Sica, C, and Cascini, L (2010) Susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides source areas using physically based models.
Springer, Vol. 53, pp. 313-332.


31. Sorbino, G, Sica, C, Cascini, L, and Cuomo, S (2007). On the forecasting of flowslides triggering areas using physically based models.
Proceedings of 1st North American Landslides Conference. Vol. 1: AEG Special Publication 23, p 305-315.

32. Tiranti, D, and Deangeli, C (2015) Modeling of debris flow depositional patterns according to the catchment and sediment souce area characteristics, fontiers in EARTH SCIENCE. Vol. 3, Article 8.

33. Wieczorek, G.F, Mandrone, G, and Decola, L (1997). The influ ence of hillslope shape on debris-flow initiation. ASCE(editor), First International Conference Water Resources Engineering Division, SanFrancisco, CA: p 21-31.

34. Yune, C.Y, Chae, Y.K, Paik, J, Kim, G, Lee, S.W, and Seo, H.S (2013) Debris flow in metropolitan area вҖ“2011 Seoul debris flow.
Journal of Mountain Science, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 199-206.