|
 |
- Search
| J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. > Volume 21(1); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Debris flow is a type of landslide that occurs mainly in mountain valley areas during heavy rainfall. Various types of barriers have been installed in South Korea to reduce the damage caused by debris flows. However, there is no reasonable design standard when installing the barrier, and an experimental study for the performance evaluation of barriers is insufficient. In this study, the performance of the net-type barrier was evaluated by analyzing the effect of the ground conditions and mesh size of the net-type barrier on the debris flow behavior by reducing the front velocity and deposition volume. As a result, for areas with less fine content, the efficiency of the net-type barrier increased as the mesh size of the net-type barrier decreased. Accordingly, the ground conditions and mesh size of the net-type barrier significantly influence the performance of the net-type barrier. The damage caused by debris flow can be sufficiently reduced through the reasonable design of a net-type barrier.
мЪФмІА
нЖ†мДЭл•ШлКФ мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞ мЛЬ мВ∞мІА мИШл°ЬлґАмЧРмДЬ м£Љл°Ь л∞ЬмГЭнХШлКФ мВ∞мВђнГЬмЭШ нХЬ мҐЕл•Шл°Ь мЪ∞л¶ђлВШлЭЉмЧРлКФ нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ м†Ак∞РнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі лЛ§мЦСнХЬ мҐЕл•ШмЭШ мВђл∞©мЛЬмД§лђЉмЭі мД§мєШлРШмЦі мЩФлЛ§. нХШмІАлІМ мВђл∞©мЛЬмД§лђЉ мД§мєШ мЛЬ нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ мД§к≥ДкЄ∞м§АмЭі м†ЬмЛЬлРШмЦі мЮИмІА мХКк≥† мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•нПЙк∞Ал•Љ мЬДнХЬ мЛ§нЧШм†Б мЧ∞кµђлПД мґ©лґДмєШ мХКмЭА мЛ§м†ХмЭілЛ§. лФ∞лЭЉмДЬ л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі мІАл∞Шм°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЧР лѓЄмєШлКФ мШБнЦ•мЭД лґДмДЭнХШмЧђ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞РмЭД нЖµнХі лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭД нПЙк∞АнХШмШАлЛ§. мЧ∞кµђ к≤∞к≥Љ, мІАл∞ШмЭШ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мЮСмЭДмИШл°Э лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭА лНФмЪ± лЖТмХШлЛ§. мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞лКФ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЧР нБ∞ мШБнЦ•мЭД м£ЉлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥Дл•Љ нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ мґ©лґДнЮИ м†Ак∞РнХ† мИШ мЮИмЭД к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь мШИмГБлРЬлЛ§.
мµЬкЈЉ мЪ∞л¶ђлВШлЭЉмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ кЄ∞нЫДл≥АнЩФмЩА лПДмЛЬнЩФл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ мВ∞мІАк∞Ьл∞Ьл°Ь мЮРмЧ∞мЮђнХі л∞ЬмГЭмЭі м¶Эк∞АнХШк≥† мЮИмЬЉл©∞ мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЮђмВ∞нФЉнХі л∞П мЭЄл™ЕнФЉнХі лШРнХЬ м¶Эк∞АнХШк≥† мЮИлЛ§. 1990лЕДлМА мЭім†ДмЧР лєДнХі 2000лЕДлМА мЭінЫД 2011лЕД мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞, 2012лЕД нГЬнТН мВ∞л∞Ф(SANBA), 2020лЕД мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞ лУ±мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі кµ≠к∞Ам†БмЬЉл°Ь лІОмЭА нФЉнХік∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХШмШАмЬЉл©∞, нКєнЮИ 2020лЕДмЧРлКФ м†Дкµ≠м†БмЬЉл°Ь 30к±імЭШ мВ∞мВђнГЬк∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХШмШАлЛ§.
нЖ†мДЭл•ШлКФ мЧђл¶Дм≤† мЪ∞кЄ∞ мЛЬ мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞л°Ь мЭЄнХі м£Љл°Ь л∞ЬмГЭнХШл©∞ к∞ХмЪ∞ мЛЬ мІАл∞ШмЬЉл°Ь лђЉмЭі мє®нИђнХШмЧђ мІАл∞ШмЭШ нБђк≥† мЮСмЭА мЮЕмЮРмЩА лђЉмЭі нШЉнХ©лРШл©імДЬ нПђнЩФлРШмЦі нЭЩмЭШ нЭРл¶ДмЭі л∞ЬмГЭнХШлКФ нШДмГБмЭД лІРнХШл©∞ м£Љл°Ь к∞АнММл•Є к≤љмВђл•Љ к∞АмІАлКФ мВ∞мІА к≥Дк≥°лґАмЧРмДЬ л∞ЬмГЭнХЬлЛ§(OвАЩBrien and Julien, 1988). лШРнХЬ мІАл∞Ш мЄµмЭі нПђнЩФлР®мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі к∞СмЮСмК§лЯљк≤М л∞ЬмГЭнХШлѓАл°Ь л∞ЬмГЭ мЛЬкЄ∞л•Љ мШИмЄ°нХШкЄ∞к∞А мֳ놵к≥† лІ§мЪ∞ лє†л•Є мЖНлПДл•Љ к∞АмІАк≥† мЭілПЩнХЬлЛ§. нКєнЮИ кµ≠лВімЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ к∞ХмЪ∞ мЛЬ мВђл©інММкіі лУ±мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі лґХкіілРЬ нЭЩмЭі мВ∞мІА мИШл°ЬлґАмЧР нЭРл•ілКФ лђЉк≥Љ нШЉнХ©лРШмЦі нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь л∞Ьм†ДлРШк≥†, нЭРл¶ДмЧР лФ∞лЭЉ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЧ∞нЦЙнЪ®к≥Љк∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХШмЧђ нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХі мВ∞мІАмЩА мЭЄм†СнХЬ лѓЉк∞А л∞П мВђнЪМкЄ∞л∞ШмЛЬмД§мЧР нБ∞ нФЉнХіл•Љ мЮЕлКФ нШХнГЬк∞А м£Љл•Љ мЭіл£®к≥† мЮИлЛ§. 2011лЕД м§СлґАмІАл∞©мЭД м§СмЛђмЬЉл°Ь нХЬ мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞л°Ь мЭЄнХі мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞, мґШм≤Ь, л∞АмЦС лУ±мЧРмДЬ мВ∞мВђнГЬк∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХШмШАк≥† мЭіл°Ь мЭЄнХі міЭ 58л™ЕмЭШ мЭЄл™ЕнФЉнХі(мВђлІЭмЮР 18л™Е)мЩА мХљ 1,500мЦµ мЫРмЭШ л≥µкµђлєДмЪ©мЭі л∞ЬмГЭнХШмШАлЛ§. лФ∞лЭЉмДЬ м†ХлґА л∞П к∞Б мІАмЮРм≤ілКФ мВ∞мВђнГЬл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ мµЬмЖМнЩФнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ лМАм±ЕлІИ놮мЧР лІОмЭА лŪ놕мЭД кЄ∞мЪЄмЭік≥† мЮИлЛ§.
мВђл∞©лМРмЭА мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь мВ∞мІА к≥Дк≥°лґАмЧР мД§мєШлРШмЦі мВ∞мВђнГЬлВШ нЩНмИШмЭШ мЪілПЩмЧРлДИмІАл•Љ к∞РмЖМмЛЬнВ§лКФ мЧ≠нХ†мЭД нХШл©∞ мВ∞мВђнГЬ мЬДнЧШмІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ м£Љл°Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ м§ДмЭікЄ∞ мЬДнХі мЛЬк≥µлРЬлЛ§. мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мҐЕл•Шл°ЬлКФ лґИнИђк≥ЉнШХ мВђл∞©лМРк≥Љ нИђк≥ЉнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭі мЮИлЛ§. к≥Љк±∞мЧРлКФ нЖ†мДЭл•ШмЭШ мЩДл≤љм∞®лЛ®мЭД мЬДнХі лґИнИђк≥ЉнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД м£Љл°Ь мЛЬк≥µнХШмШАмЬЉлВШ мµЬкЈЉмЧРлКФ к≤љкіАмД±, мГЭнГЬк≥Д мЬ†мІАкіАл¶ђ лУ±мЭШ нЩШк≤љм†Б мШБнЦ•мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі к∞Б мВ∞мІА мИШл°ЬмЭШ нКємД±мЧР лІЮк≤М лЛ§мЦСнХЬ нШХнГЬмЭШ нИђк≥ЉнШХ мВђл∞©лМРлПД мЛЬк≥µнХШк≥† мЮИлЛ§.
мВ∞мВђнГЬ л∞П нЖ†мДЭл•ШмЧР кіАнХЬ мЧ∞кµђлКФ мЪ∞л¶ђлВШлЭЉмЧР лєДнХі мВ∞мВђнГЬк∞А мЮРм£Љ л∞ЬмГЭнХШлКФ мЬ†лЯљ, м§Скµ≠, мЭЉл≥Є лУ± нХімЩЄмЧРмДЬ нШДмЮ• л™®лЛИнД∞лІБ, мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ, мИШмєШнХімДЭ, мґФм†ХмЛЭ м†ЬмХИ лУ±мЭД нЖµнХі мЭіл£®мЦім†Є мЩФлЛ§(Takahashi, 1981; Hungr et al., 2001; Rickenmann et al., 2003; Highland, 2004; Wendeler et al., 2008; Iverson et al., 2010). мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь нЖ†мДЭл•ШмЭШ мЖНлПД, нЗім†Бк±∞л¶ђ, нЗім†БлЖТмЭі, нЗім†БлґАнФЉ, мґ©к≤©мХХ лУ±мЭА нЭЩмЭШ мҐЕл•Ш(мЮРк∞И, л™®лЮШ, мДЄл¶љлґД), нХ®мИШлєД, міИкЄ∞лґАнФЉ лУ±мЧР мЭШм°інХЬлЛ§. Takahashi (1981), Hungr et al. (2001)мЭА нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нФЉнХі мШИмЄ°мЭД мЬДнХі мЛ§м†Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭ мІАл∞Ш м°∞к±імЭД нЖµнХі мІАл∞ШмЭШ мЮЕлПДлґДнПђ, нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЭРл¶ДлЖТмЭі, мИШл°Ь к≤љмВђ лУ±к≥Љ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЭРл¶ДмЖНлПДмЭШ кіАк≥Дл•Љ лґДмДЭнХШмЧђ мґФм†ХмЛЭмЭД м†ЬмХИнХШмШАлЛ§. нХШмІАлІМ мЛ§м†Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭмІАмЭШ м†Хл≥іл•Љ нЖµнХі мґФм†ХмЛЭмЭД м†ЬмХИнХШлКФ к≤ГмЭА нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭмВђл°АмЭШ нХЬк≥Д, нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭмИЬк∞ДмЭШ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±імЭД нММмХЕнХШкЄ∞ нЮШлУ§мЦі лґИнЩХмЛ§мД±мЭД к∞АмІИ мИШ мЮИлЛ§. мЭілЯђнХЬ нХЬк≥Дм†РмЭД кЈєл≥µнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі лІОмЭА мЧ∞кµђмЮРлУ§мЭА мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ мЮ•лєДл•Љ м†ЬмЮСнХШмЧђ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЧ∞кµђл•Љ мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. мК§мЉАмЭЉ мґХмЖМл•Љ нЖµнХі мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШл©і нШДмЮ•к≥Љ мЬ†мВђнХЬ мІАл∞Ш м°∞к±імЭД к∞ЦмґФмЦі мЛ§нЧШнХ† мИШ мЮИк≥† мІІмЭА мЛЬк∞ДмЧР лЛ§мИШмЭШ мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі лЛ§мЦСнХЬ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±імЧР лМАнХЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ лН∞мЭінД∞л•Љ мЦїмЭД мИШ мЮИлЛ§лКФ мЮ•м†РмЭі мЮИлЛ§. нХШмІАлІМ нШДмЮђ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЧР лМАнХЬ мЮ•лєД кЈЬл™® л∞П нШХнГЬмЭШ м†ХнЩХнХЬ кЄ∞м§АмЭі м†Хл¶љлРШмЦі мЮИмІА мХКкЄ∞ лХМлђЄмЧР мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь к∞Б мЛ§нЧШмЛ§ мЧђк±імЧР лІЮк≤М мИШл°Ь кЄЄмЭі, нШХнГЬ, нП≠, к≤љмВђ лУ±мЭД мД§м†ХнХШмЧђ мЛ§нЧШмЭі мИШнЦЙлРШк≥† мЮИлЛ§(Wendeler el al., 2008; Iverson et al., 2010; De Haas et al., 2015; Hurlimann et al., 2015). нКєнЮИ Iverson et al. (2010)мЭА нШДмЮђкєМмІА к∞АмЮ• нБ∞ кЈЬл™®мЭЄ мИШл°Ь нП≠ 2 m, мИШл°Ь лЖТмЭі 1.2 m, мИШл°Ь кЄЄмЭі 95 mмЧР лЛђнХШлКФ мЛ§вЛЕлМАнШХ мЮ•мєШл•Љ м†ЬмЮСнХШмЧђ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШк≥† нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ нКємД±мЭД нММмХЕнХШмШАлЛ§. Wendeler et al. (2008)мЭА мК§мЬДмК§мЭШ Milibach к∞ХмЧРмДЬ л∞ЬмГЭнХЬ нЖ†мДЭл•ШмЭШ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ м±ДмЈ®нХШмЧђ лЛ§мЦСнХЬ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЭШ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШк≥† міЭ 6нЪМмЭШ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. мЭімЩА к∞ЩмЭА мЛ§нЧШк≤∞к≥ЉлКФ мЧ∞кµђ лМАмГБмІАмЧ≠мЭШ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥Д л∞П кµђмґХ мЛЬ мЬ†мЪ©нХЬ м†Хл≥іл°Ь нЩЬмЪ©лРШмЧИлЛ§.
лШРнХЬ мЪ∞л¶ђлВШлЭЉмЧРмДЬлПД 2011лЕД мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мВ∞мВђнГЬ мЭінЫД мЧђлЯђ мЧ∞кµђмЮРлУ§мЧР мЭШнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЧ∞кµђк∞А нЩЬл∞ЬнЮИ мІДнЦЙлРШк≥† мЮИмЬЉл©∞ мХЮмДЬ мЦЄкЄЙнХЬ мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЭШ мЮ•м†РмЭД м†БкЈє нЩЬмЪ©нХШмЧђ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЧР кіАнХЬ мЛ§нЧШм†Б мЧ∞кµђ лШРнХЬ лІОмЭі мЭіл£®мЦім°МлЛ§(Kim et al., 2010; Eu and Im, 2017; Lee et al., 2017; Choi et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2019; Kim, 2020; Kim and Kim, 2020). Choi et al. (2018)мЭА мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЧР лМАнХЬ мКђл¶њнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ л∞∞мєШ(нШХнГЬ л∞П к∞БлПД) мШБнЦ•мЭД м°∞мВђнХШмШАк≥†, Kim et al. (2019)мЭА мЫРнЖµнШХ лМАм±Е кµђм°∞лђЉмЭД мИШл°ЬлґАмЧР мД§мєШнХШмЧђ кµђм°∞лђЉмЭШ мД§мєШл≥АнЩФ(мЫРнЖµнШХ лМАм±Е кµђм°∞лђЉмЭШ мҐЕ л∞©нЦ• мЧі к∞ЬмИШ л∞П лЖТмЭі)к∞А нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЧР лѓЄмєШлКФ мШБнЦ•мЭД лґДмДЭнХШмШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ Kim and Kim (2020)мЭА мДЬл°Ь лЛ§л•Є мІАл∞Шк≥µнХЩм†Б нКємД±мЭД к∞АмІАлКФ лСР мІАмЧ≠мЭШ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ м±ДмЈ®нХШмЧђ л†ИмШ§лѓЄнД∞ мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†л≥АлђЉмД±мЭД мВ∞м†ХнХШк≥† мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ к≤∞к≥Љл•Љ к≥†м∞∞нХШмЧђ мЬ†л≥АлђЉмД±мЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩнКємД±мЭД лґДмДЭнХШмШАлЛ§.
мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ л©Фмї§лЛИм¶ШмЭА мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ м∞®мЭіл•Љ л≥імЭЄлЛ§. лФ∞лЭЉмДЬ лМАмГБмІАмЧ≠мЭШ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ нЖµнХЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЧ∞кµђлКФ нХДмИШм†БмЬЉл°Ь мИШл∞ШлРШмЦімХЉ нХЬлЛ§. нКєнЮИ мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞, лґАмВ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ лУ±к≥Љ к∞ЩмЭА лМАлПДмЛЬмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ мВ∞мІАмЩА мЭЄм†СнХЬ мІАмЧ≠мЧР лЛ§мИШмЭШ лѓЉк∞Ак∞А л∞АмІСлРШмЦі мЮИмЦі мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞мЧР мЭШнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Шк∞А л∞ЬмГЭнЦИмЭД мЛЬ к≤љм†Ьм†БмЭЄ нФЉнХілњРлІМ мХДлЛИлЭЉ лМАкЈЬл™® мЭЄл™Е нФЉнХік∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХ† мИШ мЮИмЬЉлѓАл°Ь к∞Б мІАмЧ≠мЭШ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЭД л™ЕнЩХнЮИ кЈЬл™ЕнХімХЉ нХЬлЛ§. лШРнХЬ мЪ∞л¶ђлВШлЭЉмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нФЉнХіл•Љ м§ДмЭікЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥Д мЛЬ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД§мєШ мЬДмєШ, мҐЕл•Ш, кЈЬл™® лУ±мЧР мЮИмЦі нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ кЄ∞м§АмЭі м†ЬмЛЬлРШмЦі мЮИмІА мХКк≥† м†ДлђЄк∞АмЭШ к≤љнЧШм†Б мД§к≥ДмЧР мЭШм°інХШк≥† мЮИмЬЉл©∞, мЭілКФ мВђл∞©мЛЬмД§лђЉ мД§к≥Д мЛЬ к≥ЉлЛ§мД§к≥Дл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ к≤љм†Ьм†БмЭЄ мЖРмЛ§ л∞П нЩШк≤љ нММкііл°Ь мЭімЦімІИ мИШ мЮИлЛ§. мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЭД к≥†л†§нХЬ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ кЈЬл™®, мҐЕл•Ш, мД§мєШ мЬДмєШмЩА кіА놮лРЬ нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥ДкЄ∞м§АмЭД м†Хл¶љнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ мЧ∞кµђк∞А нХДмЪФнХЬ мЛ§м†ХмЭілЛ§.
лФ∞лЭЉмДЬ л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ лПДмЛђмІАмЩА мЭЄм†СнХЬ лґАмВ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ л∞П мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мІАмЧ≠мЭШ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ м±ДмЈ®нХЬ нЫД мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі м±ДмЈ®лРЬ мЧ∞кµђмІАмЧ≠ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙ л∞П нИђк≥ЉнШХ мВђл∞©лМР м§С нХШлВШмЭЄ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•(мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р)мЭД нПЙк∞АнХШмЧђ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞к∞А нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЭРл¶ДмЧР лѓЄмєШлКФ мШБнЦ•мЭД лґДмДЭнХШмШАлЛ§.
Fig. 1мЭА лґАмВ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞(Mt. Hwangnyeong)к≥Љ мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞(Mt. Umyeon)мЧРмДЬ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ м±ДмЈ®нХЬ мЬДмєШл•Љ лВШнГАлВЄлЛ§. мЛЬл£М м±ДмЈ® мЬДмєШлКФ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ л∞П мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мІАмЧ≠мЭШ мВ∞мВђнГЬ мЬДнЧШмІАлПДмЩА мВ∞мВђнГЬ мݳ놕мЭД к≤АнЖ†нХШмЧђ к∞Б мВ∞мІАмЧРмДЬ мВ∞мВђнГЬ л∞ЬмГЭ мЬДнЧШмЭі нБ∞ мІАмЧ≠мЭШ мГБл•ШлґАл°Ь мД†м†ХнХШмШАлЛ§(Pradhan et al., 2018; Ngyuen and Kim, 2019). Table 1мЧР м±ДмЈ®лРЬ к∞Б мЛЬл£МмЭШ мІАл∞Шк≥µнХЩм†Б нКємД±мЭД лПДмЛЬнХШмШАлЛ§. мЮЕлПДлґДнПђмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі мХљ 72.6%, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мХљ 24.5%л°Ь мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі нЫ®мФђ лІОмХШлЛ§. мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭДмИШл°Э мХ°мД±нХЬк≥ДлКФ нБђк≤М лВШнГАлВЬлЛ§. мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Д 48.8%, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Д 33.3%л°Ь нЩХмЧ∞нХЬ м∞®мЭіл•Љ л≥імШАлЛ§. нЖ†мДЭл•ШлКФ мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞ мЛЬ лђЉмЭі мІАл∞ШмЬЉл°Ь мє®нИђнХШл©імДЬ нЭЩ мЮЕмЮРмЩА лђЉмЭі нШЉнХ©лРШк≥† мЬ†м≤ім≤ШлЯЉ к±∞лПЩнХШмЧђ нЭРл¶ДмЭі л∞ЬмГЭнХШлКФ нШДмГБмЬЉл°Ь мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Д мЭімГБмЭШ нХ®мИШлєДмЧРмДЬ л∞ЬмГЭнХЬлЛ§. м¶Й, нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЩА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мІАл∞Шк≥µнХЩм†Б нКємД±мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Дк∞А мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі лЖТк≥† мЭілКФ к≥І мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£Мк∞А мЬ†м≤ім≤ШлЯЉ к±∞лПЩнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ кЄ∞л≥Є нХ®мИШлєДк∞А лНФ нБђлЛ§к≥† л≥Љ мИШ мЮИлЛ§.
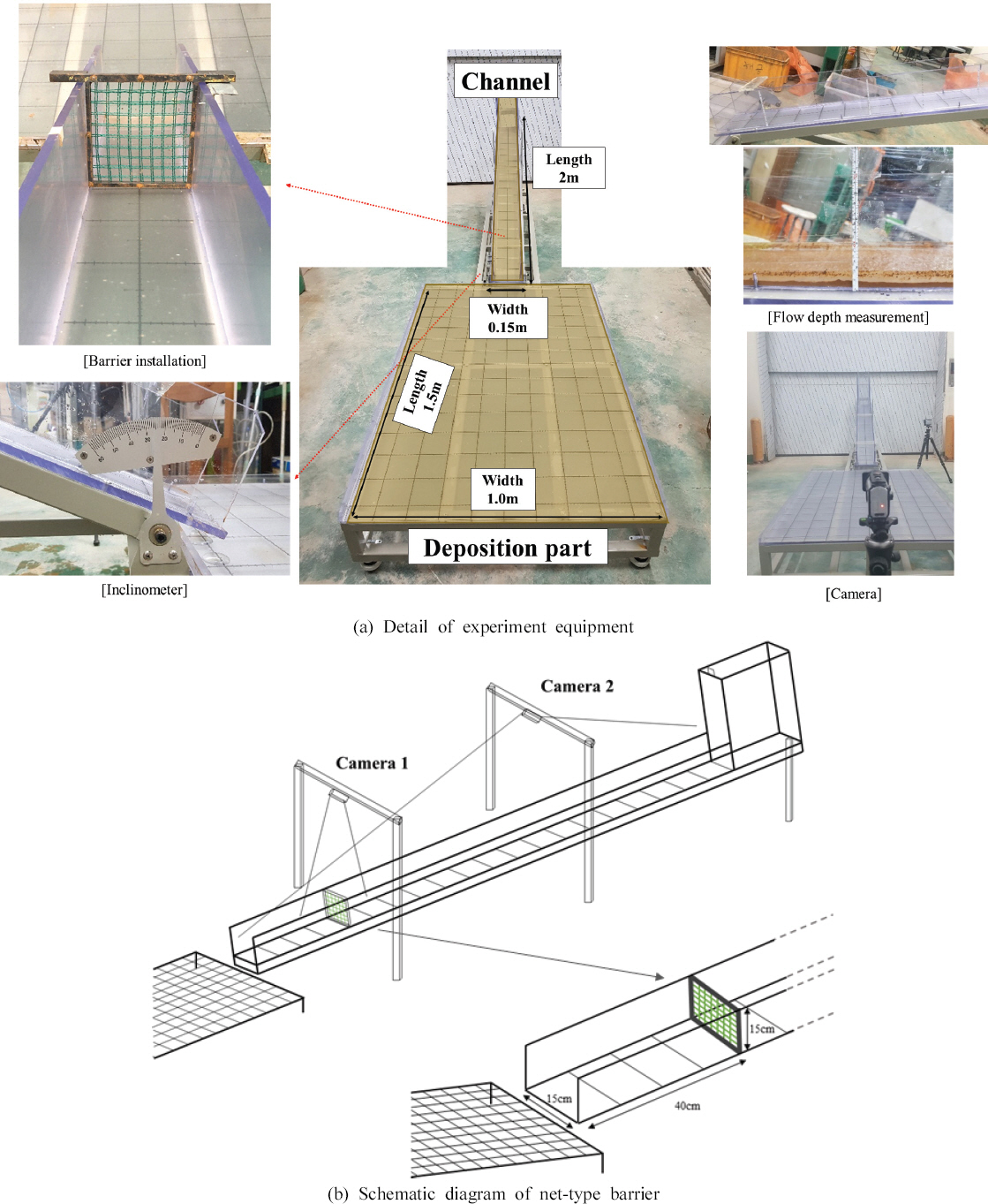
л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬ мВђмЪ©нХЬ мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ мЮ•лєД(small-scale debris flow experiment equipment)лКФ Fig. 2мЩА к∞ЩлЛ§. Fig. 2(a)мЭШ мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ мЮ•лєДлКФ к≤љмВђ м°∞м†ИмЭі к∞АлК•нХШлЛ§.(17¬∞-45¬∞) нП≠ 0.15 m, кЄЄмЭі 2 mмЭШ мВђк∞Б лЛ®л©імЬЉл°Ь мИШл°Ьк∞А м†ЬмЮСлРШмЧИмЬЉл©∞ мИШл°Ь мГБлґАмЧРлКФ мЛ§нЧШмЛЬл£МмЧР нЭРл¶ДмЭД л∞ЬмГЭмЛЬнВ§кЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ нП≠ 0.15 m, кЄЄмЭі 0.4 m, лЖТмЭі 0.4 mмЭШ мЛЬл£МмГБмЮР(soil box)к∞А мЧ∞к≤∞лРШмЦі мЮИлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нЗім†БлґАнФЉл•Љ мХМмХДл≥ікЄ∞ мЬДнХШмЧђ нП≠ 1.0 m, кЄЄмЭі 1.5 mмЭШ нЗім†БлґА(deposition part)лПД м†ЬмЮСлРШмЧИлЛ§. мИШл°ЬлґА л∞П нЗім†БлґАмЧРлКФ 10 cm к∞Дк≤©мЬЉл°Ь м£Љ лИИкЄИмЭі, 1 cm к∞Дк≤©мЬЉл°Ь л≥ім°∞лИИкЄИмЭі нСЬмЛЬлРШмЦі мЮИмЦі, мИШл°ЬлґА міђмШБ мШБмГБмЭД нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДл•Љ, нЗім†БлґАмЧР нЗім†БлРЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЗім†Б лЖТмЭіл•Љ нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЗім†БлґАнФЉл•Љ мЄ°м†ХнХШмШАлЛ§.
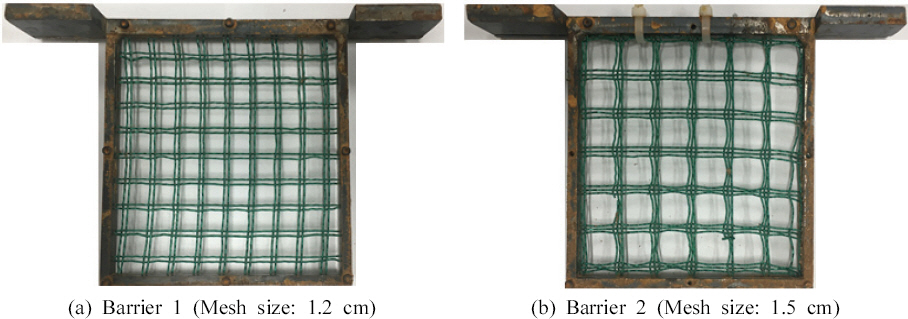
лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД§мєШл•Љ нЖµнХЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ м†Ак∞Р нЪ®к≥Љл•Љ лґДмДЭнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ мЮ•лєДмЧР лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмЧђ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШмЧР лФ∞л•Є мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЮ•лєДмЭШ л™®мЛЭлПДлКФ Fig. 2(b)мЩА к∞ЩлЛ§. лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД§мєШ мЬДмєШлКФ мИШл°Ь нХШлЛ®лґАмЧРмДЬ 40 cm лЦ®мЦімІД мІАм†РмЭіл©∞ мВђл∞©лМР м†ДвЛЕнЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДл•Љ мДЄлґАм†БмЬЉл°Ь кіАм∞∞нХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі мИШл°Ь мГБлЛ®мЧР лСР лМАмЭШ мєіл©ФлЭЉл•Љ мД§мєШнХШмЧђ мШБмГБмЭД міђмШБнХШмШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш м†Ак∞Р нЪ®к≥Љл•Љ лґДмДЭнХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А лЛ§л•Є лСР лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД м†ЬмЮСнХШмШАмЬЉл©∞(Fig. 3), м†ЬмЮСлРЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЮ•лєДмЧР мД§мєШнХЬ нЫД мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмЧђ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ м†Ак∞Р нЪ®к≥Љл•Љ лґДмДЭнХШмШАлЛ§.
мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЧРмДЬ л≥АнЩФ к∞АлК•нХЬ мЛ§нЧШ м°∞к±імЭА мЛЬл£МмЭШ нХ®мИШлєД, міИкЄ∞лґАнФЉ, мЛ§нЧШмЮ•лєДмЭШ мИШл°Ьк≤љмВђ, мЮЕлПДлґДнПђ л≥АнЩФмЧР лФ∞л•Є мЮРк∞И, л™®лЮШ л∞П мДЄл¶љлґДмЭШ кµђмД±лєД лУ±мЭі мЮИлЛ§. л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ лґАмВ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ л∞П мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞мЧРмДЬ м±ДмЈ®лРЬ мХ°мД±нХЬк≥ДмЭШ м∞®мЭік∞А мЮИлКФ лСР мЛЬл£МмЭШ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЭД л≥АнЩФмЛЬмЉЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЭД лґДмДЭнХШмШАлЛ§. Table 2лКФ мЛ§нЧШ мЛЬ м†БмЪ©лРЬ лСР мЛЬл£МмЭШ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞ лУ±мЭШ мЛ§нЧШм°∞к±імЭД лВШнГАлВЄлЛ§. нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЭА к∞Б мЛЬл£МмЭШ мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Д мЭімГБмЭШ нХ®мИШлєДмЧРмДЬ л™®мВђлРЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Шк∞А мИШл°Ьл•Љ нЖµк≥ЉнХШмЧђ нЗім†БлґАкєМмІА мґ©лґДнЮИ нЭРл•Љ мИШ мЮИлКФ м°∞к±імЬЉл°Ь мД§м†ХлРШмЧИлЛ§. лШРнХЬ л™®лЮШ л∞П мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЧР лєДнХі мЮРк∞ИмЭШ нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЦі мЛЬл£МмЭШ мЭЉкіАмД±мЭі лЦ®мЦімІАк≥† л∞Шл≥µ мЛ§нЧШ мЛЬ к≤∞к≥ЉмЭШ нЖµмЭЉмД±мЭі лґАм°±нХ† к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь нМРлЛ®лРШмЦі, нШДмЮ•мЧРмДЬ м±ДмЈ®лРЬ нТНнЩФнЖ† мЛЬл£Мл•Љ мЩДм†Д к±ім°∞нХЬ нЫД 4л≤Им≤іл°Ь нЖµк≥ЉмЛЬнВ® л™®лЮШмЩА мДЄл¶љлґДлІМмЭД мЭімЪ©нХШмЧђ мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ нЫД нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЭА мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±і мЭілВіл°Ь мД§м†ХнХШмЧђ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞ 60%мЧРмДЬ 70%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 3к∞АмІА м°∞к±імЬЉл°Ь мИШнЦЙлРШмЧИк≥† к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.2 cmмЭЄ Barrier 1мЭД мД§мєШнХШмЧђ 63%мЧРмДЬ 68%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 3к∞АмІА м°∞к±і, к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.5 cmмЭЄ Barrier 2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ нЫД 62%мЧРмДЬ 68%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 3к∞АмІА м°∞к±імЬЉл°Ь мЛ§нЧШмЭі мИШнЦЙлРШмЦі к∞Бк∞Б 3нЪМмФ© міЭ 27нЪМ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞лПД нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мЛ§нЧШк≥Љм†Хк≥Љ лПЩмЭЉнХШк≤М мЛ§нЧШмЭД мІДнЦЙнХШмШАмЬЉл©∞ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞ 40%мЧРмДЬ 52%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 6к∞АмІА м°∞к±імЬЉл°Ь мИШнЦЙлРШмЧИк≥† к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.2 cmмЭЄ Barrier 1мЭД мД§мєШнХШмЧђ 45%мЧРмДЬ 52%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 3к∞АмІА м°∞к±і, к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.5 cmмЭЄ Barrier 2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ нЫД 42%мЧРмДЬ 49%мЭШ нХ®мИШлєД л≤ФмЬДмЧРмДЬ 3к∞АмІА м°∞к±імЬЉл°Ь мЛ§нЧШмЭі мИШнЦЙлРШмЧИлЛ§. лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞мЩА лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХЬ нЫД к∞Б 3нЪМмФ© міЭ 36нЪМ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмЧђ мЛ§нЧШк≤∞к≥ЉмЧР лМАнХЬ мЛ†лҐ∞мД±мЭД нЩХл≥інХШмШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±і, мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ мЬ†вЛЕлђі л∞П к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞л•Љ м†ЬмЩЄнХЬ міИкЄ∞лґАнФЉ(8,600 cm3), мИШл°Ь к≤љмВђ(30¬∞) лУ±мЭШ мЛ§нЧШ м°∞к±імЭА лПЩмЭЉнХШк≤М мД§м†ХнХШмШАлЛ§.
Experiment Condition
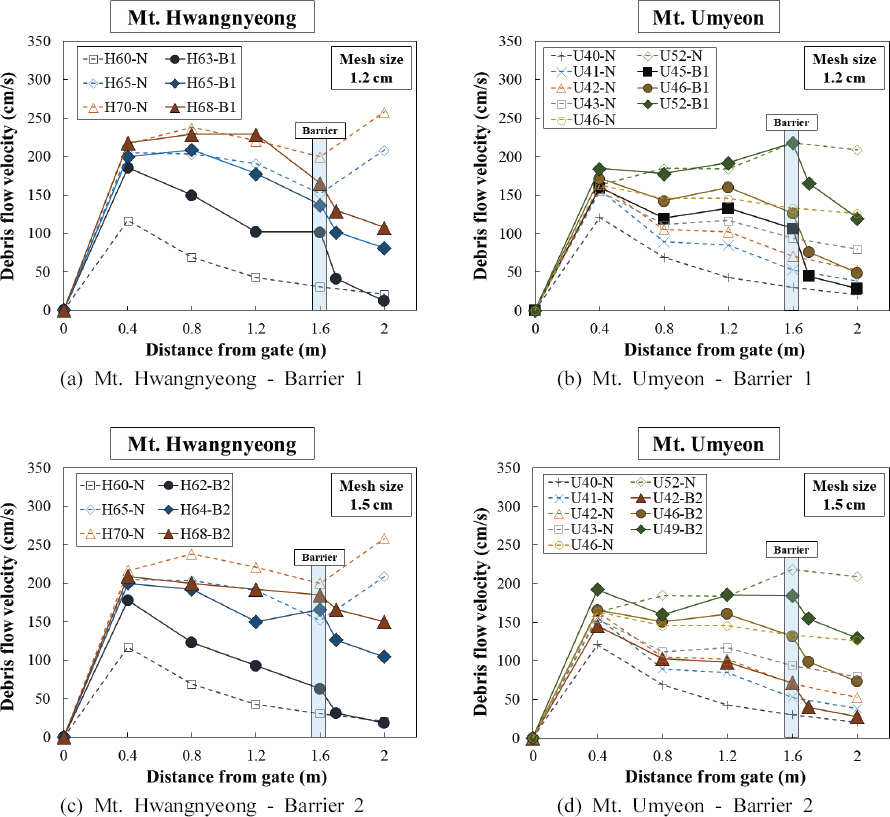
лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШмЧР лФ∞л•Є к∞Б мЛЬл£МмЭШ мЛ§нЧШмЮ•лєД мИШл°ЬлґА нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПД л≥АнЩФл•Љ Fig. 4мЧР лВШнГАлВімЧИлЛ§. мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞л•Љ N (No barrier), к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.2 cmмЭЄ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД B1 (Barrier 1), к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А 1.5 cmмЭЄ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД B2 (Barrier 2)лЭЉк≥† м†ХмЭШнХШмШАлЛ§. лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД нЖµк≥ЉнХЬ мІБнЫДмЭШ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДлКФ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш нЭРл¶ДмЭі лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЧР мґ©лПМнХ† лХМмЭШ мґ©к≤©мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі лЛ§мЖМ мШ§м∞®к∞А л∞ЬмГЭнХШлѓАл°Ь мХЮмДЬ 3.2м†ИмЧР мЦЄкЄЙ нХЬ л∞ФмЩА к∞ЩмЭі к∞Б нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ мИШнЦЙлРЬ 3нЪМмЭШ л∞Шл≥µмЛ§нЧШ к≤∞к≥Љл•Љ нПЙкЈ†нХШмЧђ мВ∞м†ХнХШмШАлЛ§.
мЛ§нЧШ к≤∞к≥Љ нЖ†мДЭл•Шк∞А лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД нЖµк≥ЉнХЬ мІБнЫД мИШл°Ь 1.6 m мІАм†РмЧРмДЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДлКФ кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. B1мЭД мД§мєШнЦИмЭД лХМ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДлКФ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мµЬмЖМ 35 cm/sмЧРмДЬ мµЬлМА 61 cm/s, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мµЬмЖМ 53 cm/sмЧРмДЬ мµЬлМА 62 cm/sкєМмІА к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ B2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мµЬмЖМ 19 cm/sмЧРмДЬ мµЬлМА 31 cm/s, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мµЬмЖМ 29 cm/sмЧРмДЬ мµЬлМА 34 cm/sкєМмІА к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§. мЭімЩА к∞ЩмЭі лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ мЛЬ мИШл°ЬлґАмЧРмДЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДлКФ к∞Б нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЧР мЭШнХі мЖНлПДк∞А кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤љнЦ•мЭД л≥імШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нЩ©л†ємВ∞мЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР нЖµк≥Љ мІБнЫД мЖНлПД к∞РмЖМк∞А нБђк≥† лСР мЛЬл£М л™®лСР B2мЧР лєДнХі к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мЮСмЭА B1мЭД мД§мєШнХШмШАмЭД лХМ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДк∞А лНФмЪ± кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§.
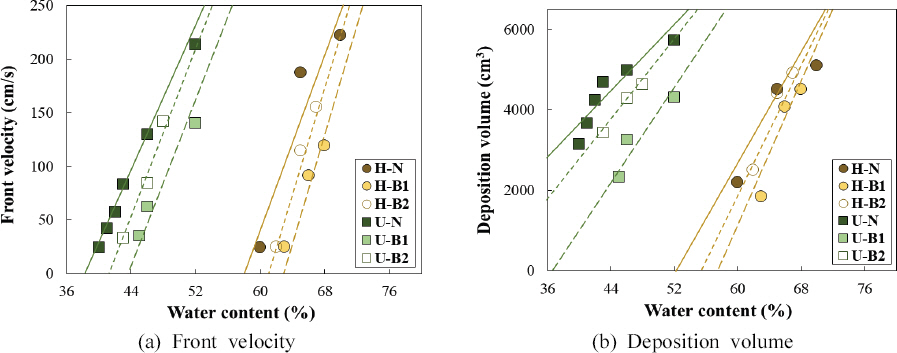
мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШ мЛЬ нЖ†мДЭл•ШмЭШ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДлКФ мИШл°Ь нХШлЛ®лґА мЖНлПДл•Љ нЖµнХі мВ∞м†ХлРЬлЛ§(Prochaska et al., 2008; Eu and Im, 2017). л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ міЭ 2.0 mмЭШ мИШл°ЬлґАл•Љ 0.4 m к∞Дк≤© лЛ§мДѓ к∞ЬмЭШ кµђк∞ДмЬЉл°Ь лВШлИДмЦі мИШл°ЬлґА лБЭлЛ® лІИмІАлІЙ кµђк∞ДмЭШ нПЙкЈ†мЖНлПДл•Љ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДл°Ь м†ХмЭШнХШмШАлЛ§. Fig. 5мЧР мІАл∞Шм°∞к±і л∞П лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЩА нЗім†БлґАнФЉл•Љ лПДмЛЬнХШмШАлЛ§. B1мЭД мД§мєШнЦИмЭД лХМ, нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЭШ к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДлКФ 73 cm/sмЧРмДЬ 85 cm/s, нЗім†БлґАнФЉмЭШ к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДлКФ 1,514 cm3мЧРмДЬ 1,656 cm3мЭілЛ§. мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ 61 cm/sмЧРмДЬ 78 cm/sмЭШ к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДл•Љ л≥імШАмЬЉл©∞, нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ 1,541 cm3мЧРмДЬ 2,227 cm3мЭШ к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДк∞А лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. лШРнХЬ, B2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДлКФ 29 cm/sмЧРмДЬ 61 cm/s, нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ 287 cm3мЧРмДЬ 564 cm3мЭШ к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДк∞А лВШнГАлВђмЬЉл©∞, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД к∞РмЖМл≤ФмЬДлКФ 13 cm/sмЧРмДЬ 43 cm/s, нЗім†БлґАнФЉмЭШ к∞РмЖМ л≤ФмЬДлКФ 557 cm3мЧРмДЬ 790 cm3мЭілЛ§. мЭімЩА к∞ЩмЭі лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ мЛЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЩА нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ к∞Б нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЧР мЭШнХі кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤љнЦ•мЭД л≥імШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ лСР мЛЬл£М л™®лСР B2мЧР лєДнХі к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мЮСмЭА B1мЭД мД§мєШнХШмШАмЭД лХМ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЩА нЗім†БлґАнФЉк∞А лНФмЪ± нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШмШАмЬЉл©∞, нЩ©л†ємВ∞мЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД лМАлєД нЗім†БлґАнФЉк∞А лНФмЪ± нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. лґДмДЭ к≤∞к≥Љ, лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мЮСмЭДмИШл°Э нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉк∞А лНФ кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђмЬЉл©∞, нКєнЮИ нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧРмДЬ лНФмЪ± кЄЙк≤©нХШк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нХ®мИШлєДк∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ†мИШл°Э, к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мї§мІИмИШл°Э лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭА нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШмЧђ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞мЭШ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ к≤∞к≥ЉмЧР м†Рм†Р мИШл†інХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§.
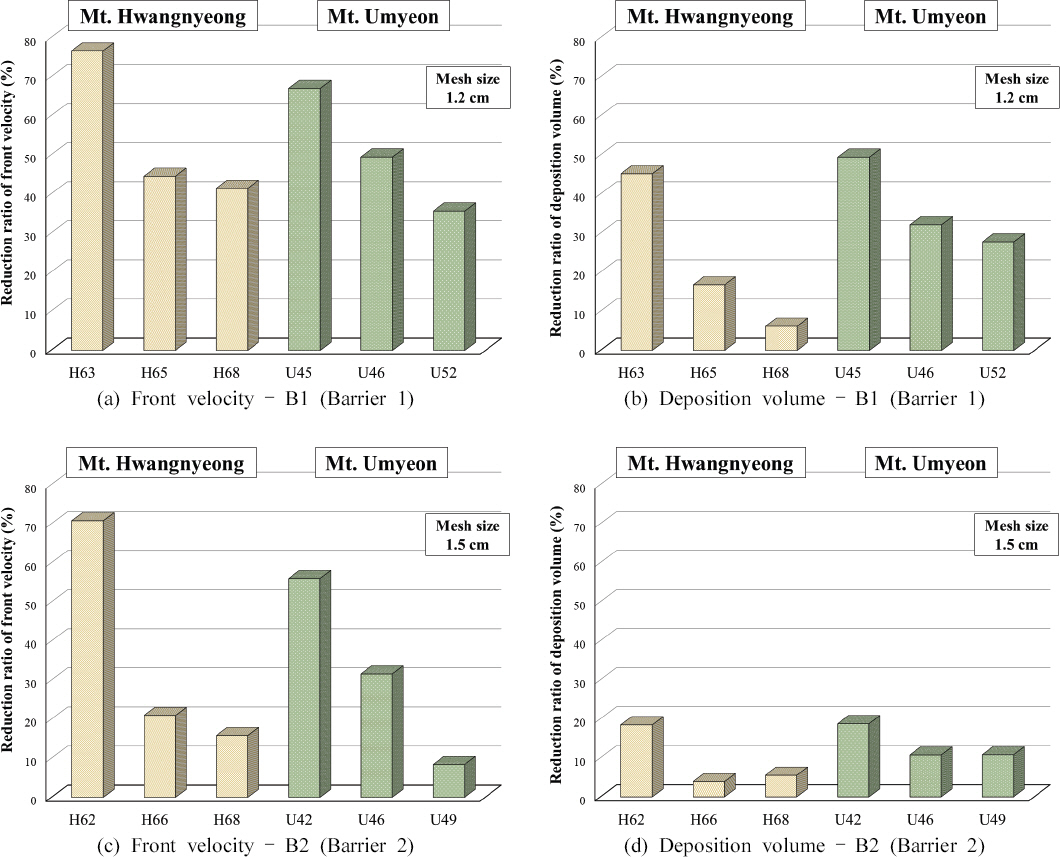
к∞Б нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬмЭШ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭД Fig. 5мЧР лВШнГАлВЄ мЛ§нЧШк≤∞к≥ЉмЭШ нЪМкЈАмД†мЭД мЭімЪ©нХЬ лєДкµРлґДмДЭмЭД нЖµнХі Fig. 6мЧР лІЙлМАкЈЄлЮШнФДл°Ь лВШнГАлВімЧИлЛ§. нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭД мД§мєШнХШмІА мХКмЭА к≤љмЪ∞мЭШ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ к≤∞к≥ЉмЧР лМАнХЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ нЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ к∞РмЖМл•Љ лєДмЬ®л°Ь лВШнГАлВімЧИлЛ§. мД§мєШ нЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш м†Ак∞РмЭД л®Љм†А, B1мЭД мД§мєШнХЬ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧР лФ∞лЭЉ 76%мЧРмДЬ 41%л°Ь мХљ 35%, мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 66%мЧРмДЬ 35%л°Ь мХљ 31% мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЭі к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§. B2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ нХ®мИШлєДк∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ®мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА 70%мЧРмДЬ 15%л°Ь мХљ 55% к∞РмЖМнХШмШАк≥† мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 55%мЧРмДЬ 8%л°Ь мХљ 47% к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нЗім†БлґАнФЉмЭШ к≤љмЪ∞ B1мЭД мД§мєШнЦИмЭД лХМ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 45%мЧРмДЬ 6%л°Ь 39% к∞РмЖМнХШмШАк≥† мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 49%мЧРмДЬ 27%л°Ь мХљ 22% к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§. B2л•Љ мД§мєШнХЬ к≤љмЪ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 18%мЧРмДЬ 3%л°Ь мХљ 15% нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭі к∞РмЖМнХШмШАк≥† мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ 18%мЧРмДЬ 10%л°Ь мХљ 8% к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§.
лґДмДЭ к≤∞к≥Љ, к∞Б мЛЬл£МмЭШ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭШ к∞РмЖМ к≤љнЦ•мЭА лЛ§мЖМ лєДмКЈнХШк≤М лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. нХШмІАлІМ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мї§мІИмИШл°Э нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭі нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђмЬЉл©∞, мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЧР лєДнХі нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА лІ§мЪ∞ лВЃк≤М лВШнГАлВШлКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§. лШРнХЬ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ нХ®мИШлєДк∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ®мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЭі кЄЙк≤©нХШк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤љнЦ•мЭД л≥імШАмЬЉл©∞, нКєнЮИ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЧР лєДнХі нХ®мИШлєД м¶Эк∞АмЧР лФ∞л•Є нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі нЫ®мФђ лВЃмЭА к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВШ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧРмДЬмЭШ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД±лК•мЭі лНФ лЖТмЭА к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§.
нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭ мЛЬ нЖ†мДЭл•ШлКФ л∞ЬмГЭ мВ∞мІА мЭЄкЈЉмЭШ лПДмЛђмІАмЧР нЗім†БлРШл©імДЬ лІЙлМАнХЬ мЭЄл™Е л∞П мЮђмВ∞ нФЉнХіл•Љ мЮЕнЮИк≤М лРШл©∞ мЭілХМ нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХі м†ХлПДл•Љ мШИмЄ°нХ† мИШ мЮИлКФ м≤ЩлПДл°Ь мВђмЪ©лРЬлЛ§(H√Љbl et al., 2009). лШРнХЬ, мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЭА мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧР лєДнХі мХ°мД±нХЬк≥Дк∞А мЮСк≥† к∞ЩмЭА нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ мЮСмЭА м†РмД±к≥Љ нХ≠л≥µмЭС놕мЭД к∞АмІАлѓАл°Ь к∞ЩмЭА к∞ХмЪ∞мЧРмДЬ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЭШ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭмЬДнЧШмЭі нБђлЛ§(Kim and Kim, 2020). л≥Є мЧ∞кµђл•Љ нЖµнХі лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭА мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙ л∞П лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР нБђк≤М мШБнЦ•мЭД л∞Ык≥† лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ мЛЬ мД§мєШмІАмЧ≠мЭШ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЭД мґ©лґДнЮИ к≥†л†§нХШмЧђ мД§к≥ДнХімХЉ нХЬлЛ§лКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§. мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭА лНФ лЖТмХШмЬЉл©∞, к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ†мИШл°Э кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§. мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЭД к≥†л†§нХЬ нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ кЈЬл™®мЭШ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥Д л∞П мД§мєШл•Љ нЖµнХі к≤љм†ЬмД± нЩХл≥інХ®к≥Љ лПЩмЛЬмЧР мґФнЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш л∞ЬмГЭ мЛЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ мґ©лґДнЮИ м†Ак∞РнХ† мИШ мЮИмЭД к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь мШИмГБлРЬлЛ§.
л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ лґАмВ∞ нЩ©л†ємВ∞ л∞П мДЬмЪЄ мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ м±ДмЈ®нХЬ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ мЭімЪ©нХШмЧђ мЖМнШХ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЛ§нЧШмЭД нЖµнХі мІАл∞Ш м°∞к±і л∞П к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ м†ДвЛЕнЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ(мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ)мЭД лґДмДЭнХШмЧђ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭД нПЙк∞АнХШмШАлЛ§.
(1) лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР нЖµк≥Љ мІБнЫД мИШл°ЬлґАмЧРмДЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДлКФ кЄЙк≤©нХШк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђмЬЉл©∞, нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЭШ мИШл°ЬлґА нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЖНлПДк∞А лНФ нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШмШАлЛ§.
(2) нЩ©л†ємВ∞к≥Љ мЪ∞л©імВ∞ лСР мЛЬл£М л™®лСР лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШл°Ь мЭЄнХі к∞Б нХ®мИШлєД м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПДмЩА нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ кЄЙк≤©нЮИ к∞РмЖМнХШмШАмЬЉл©∞, B2мЧР лєДнХі к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А мЮСмЭА B1мЭД мД§мєШнХШмШАмЭД лХМ лНФмЪ± нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§. лШРнХЬ нЗім†БлґАнФЉлКФ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£Мк∞А нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі лНФмЪ± нБђк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь лВШнГАлВђлЛ§.
(3) к∞Б мЛЬл£МмЭШ мІАл∞Шм°∞к±ік≥Љ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮР нБђкЄ∞мЧР лФ∞л•Є мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД л∞П нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭШ к∞РмЖМ к≤љнЦ•мЭА лЛ§мЖМ лєДмКЈнХШк≤М лВШнГАлВђмЬЉлВШ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЧР лєДнХі нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА лЛ§мЖМ лВЃк≤М лВШнГАлВђлЛ§.
(4) мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА нЩ©л†ємВ∞ мЛЬл£МлКФ нХ®мИШлєДк∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ®мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЧР лєДнХі мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЭі кЄЙк≤©нХШк≤М к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤љнЦ•мЭД л≥імШАлЛ§. нКєнЮИ мЬ†мґЬмЖНлПД м†Ак∞Р땆мЧР лМАлєД нЗім†БлґАнФЉ м†Ак∞Р땆мЭА мЪ∞л©імВ∞ мЛЬл£МмЩА лєДкµРнХШмШАмЭД лХМ лІ§мЪ∞ лВЃк≤М лВШнГАлВШлКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§.
(5) л≥Є мЧ∞кµђ к≤∞к≥Љл•Љ нЖµнХі, лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ мД±лК•мЭА мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі лІОмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧР лєДнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЭі м†БмЭА мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ лНФ лЖТлЛ§лКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИмЬЉл©∞, лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ к≤©мЮРнБђкЄ∞к∞А м¶Эк∞АнХ†мИШл°Э к∞РмЖМнХШлКФ к≤ГмЭД мХМ мИШ мЮИмЧИлЛ§. мЭімЧР лФ∞лЭЉ нХ©л¶ђм†БмЭЄ кЈЬл™®мЭШ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§к≥Дл•Љ нЖµнХі нЖ†мДЭл•Шл°Ь мЭЄнХЬ нФЉнХіл•Љ мґ©лґДнЮИ м†Ак∞РнХ† мИШ мЮИмЭД к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь мШИмГБлРЬлЛ§.
л≥Є мЧ∞кµђлКФ мЛ§лВімЛЬнЧШмЭД нЖµнХі мДЄл¶љлґД нХ®мЬ†лЯЙ м∞®мЭімЧР мЭШнХЬ мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЧР лФ∞л•Є лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШ м†ДвЛЕнЫД нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЭД лєДкµРнХШмЧђ лґДмДЭнХЬ к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь мІСм§Ск∞ХмЪ∞ мЛЬ мДЬл°Ь лЛ§л•Є мІАл∞ШнКємД±мЭД к∞АмІД мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД§мєШмЧР лФ∞л•Є нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЭД мШИмЄ°нХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХЬ кЄ∞міИмЮРл£Мл°Ь нЩЬмЪ©лР† мИШ мЮИмЭД к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь кЄ∞лМАлРЬлЛ§. нХШмІАлІМ л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЧРмДЬлКФ мЭімГБм†БмЭЄ мИШл°ЬнШХнГЬл•Љ к∞АмІД мЮ•лєДл•Љ мЭімЪ©нХШмЧђ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАк≥† мЛЬл£МмЭШ міИкЄ∞лґАнФЉ, мИШл°Ьк≤љмВђ лУ±мЭШ м°∞к±імЭД лПЩмЭЉнХШк≤М м†БмЪ©нХШмЧђ мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХШмШАлЛ§. лШРнХЬ мЧ∞кµђ лМАмГБ мІАмЧ≠мЧРмДЬ лґАлґДм†БмЬЉл°Ь м±ДмЈ®нХЬ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ мВђмЪ©нХШмШАмЬЉлѓАл°Ь л≥Є мЧ∞кµђмЭШ мЛ§нЧШк≤∞к≥Љл•Љ нЖµнХі мЛ§м†Ь нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩ л∞П лД§нКЄнШХ мВђл∞©лМР мД±лК•мЭД мШИмЄ°нХШкЄ∞мЧРлКФ нХЬк≥Дк∞А мЮИлЛ§. кЈЄлЯђлѓАл°Ь мґФнЫД мИШмєШнХімДЭм†Б мЧ∞кµђл•Љ нЖµнХі мЛ§м†Ь мВ∞мІАмЧРмДЬмЭШ нЖ†мДЭл•Ш к±∞лПЩмЭД мШИмЄ°нХШмЧђ мЛ§лВі мЛ§нЧШ к≤∞к≥ЉмЩА лєДкµР к≤Ам¶ЭмЭД нХ† нХДмЪФмД±мЭі мЮИлЛ§. лШРнХЬ, мВђл∞©лМРмЭШ м°∞к±і(мВђл∞©лМР мҐЕл•Ш, мД§мєШмЬДмєШ лУ±)мЭД лЛ§мЦСнХШк≤М мД§м†ХнХШк≥† мЮРк∞И л∞П мЬ†л™©мЭД нПђнХ®нХЬ мЛЬл£Мл•Љ м°∞мД±нХШмЧђ мЮРк∞И лШРлКФ мЬ†л™©мЭШ нБђкЄ∞ л∞П нХ®мЬ†лЯЙмЧР лФ∞л•Є мВђл∞©лМР мД±лК•мЧР лМАнХЬ мґФк∞А мЛ§нЧШмЭД мИШнЦЙнХЬлЛ§л©і лНФмЪ± мДЄл∞АнХЬ мВђл∞©лМР мД±лК• мШИмЄ°вЛЕлґДмДЭмЭі нХДмЪФнХ† к≤ГмЬЉл°Ь мВђл£МлРЬлЛ§.
к∞РмВђмЭШ кЄА
мЭі лЕЉлђЄмЭА лґАк≤љлМАнХЩкµР мЮРмЬ®м∞љмЭШнХЩмИ†мЧ∞кµђлєД(2019лЕД)мЧР мЭШнХШмЧђ мЧ∞кµђлРШмЧИмЭМ.
References
1. Choi, S.K, Lee, J.M, and Kwon, T.H (2018) Effect of slit-type barrier on characteristics of water-dominant debris flows:small-scale physical modeling. Landslides, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 111-122.


2. De Haas, T, Braat, L, Leuven, J.R, Lokhorst, I.R, and Kleinhans, M.G (2015) Effects of debris flow composition on runout, depositional mechanisms, and deposit morphology in laboratory experiments. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, Vol. 120, No. 9, pp. 1949-1972.

3. Eu, S, and Im, S (2017) Examining velocity estimation equations of debris flow using small-scaled flume experiments. Journal of Korean Forest Society, Vol. 106, No. 4, pp. 424-430.

4. Highland, L (2004) Landslide types and processes, Reston, VA, USA: USGS Fact Sheet 2004-3072, U.S. Geological Survey.

5. H√Љbl, J, Suda, J, Proske, D, Kaitna, R, and Scheidl, C (2009) Debris flow impact estimation. In C. Popovska, and C. Jovanovski (Eds.). Eleventh international symposium on water management and hydraulic engineering, Vol. 1, pp. 137-148.

6. Hungr, O, Evans, S.G, Bovis, M.J, and Hutchinson, J.N (2001) A review of the classification of landslides of the flow type. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience, Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 221-238.


7. Hurlimann, M, McArdell, B.W, and Rickli, C (2015) Field and labora tory analysis of the runout characteristics of hillslope debris flows in Switzerland. Geomorphology, Vol. 232, pp. 20-32.

8. Iverson, R.M, Logan, M, LaHusen, R.G, and Berti, M (2010) The perfect debris flow?Aggregated results from 28 large-scale experiments. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, Vol. 115, No. F3, pp. F03005 doi:10.1029/2009JF001514.


9. Kim, B.J, Han, K.D, Kim, H.S, Choi, C.E, and Yune, C.Y (2019) An experimental study on cylindrical countermeasures for dissipation of debris flow energy. Journal of the Korean Geo-Environmental Society, Vol. 20, No. 1, pp. 57-65.

10. Kim, H.J (2020) An experimental study to analyze the behavioral characteristics of debris flow according to the rheological properties of the soil. Master's thesis, PuKyong National University.

11. Kim, H.J, and Kim, Y.T (2020) Debris flow behavioral characteristic based on rheological properties:a case study on Mt. Hwangnyeong and Mt. Umyeon. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig, Vol. 20, No. 4, pp. 75-85.


12. Kim, J.H, Lee, Y.S, and Park, K.B (2010) A study on model experiment for evaluation of debris flow's impact force characteristics. Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society, Vol. 26, No. 11, pp. 5-15.

13. Lee, K.S, Cho, S.H, Kim, J.H, and Yoo, B.S (2017) Estimation of debris flow impact forces on mitigation structures using small-scale modelling. The Journal of Engineering Geology, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 191-205.

14. Ngyuen, V.B.Q, and Kim, Y.T (2019) Rainfall-earthquake- induced landslide hazard prediction by monte carlo simulation:a case study of MT. Umyeon in Korea. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 24, No. 1, pp. 73-86.


15. O'Brien, J.S, and Julien, P.Y (1988) Laboratory analysis of mudflow properties. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, Vol. 114, No. 8, pp. 877-887.

16. Pradhan, A.M.S, Lee, S.R, and Kim, Y.T (2018) A shallow slide prediction model combining rainfall threshold warnings ans shallow slide susceptibility in Busan, Korea. Landslides, Vol. 16, pp. 647-659.


17. Prochaska, A.B, Santi, P.M, Higgins, J.D, and Cannon, S.H (2008) A study of methods to estimate debris flow velocity. Landslides, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 431-444.


18. Rickenmann, D, Weber, D, and Stepanov, B (2003) Erosion by debris flows in field and laboratory experiments. In: Rickenmann D, Chen C. I, eds. Debris-flow hazards mitigation:mechanics, prediction, and assessment. Proceedings of the 3th International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation, pp. 883-894. Davos, Switzerland.

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 2,074 View
- 42 Download
- Related articles in KOSHAM
-
Effect of Barrier Location on Debris Flow Behaviors: A Numerical Study2017 December;17(6)